Fig. 3.
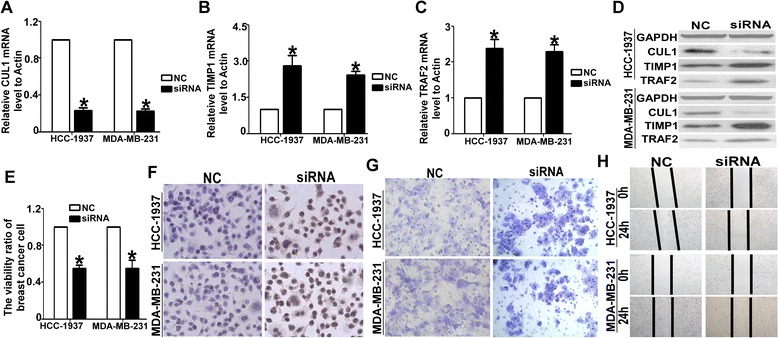
Knocked-down the CUL1 lead to the same effect of Selumetinib. a The siRNA could effective inhibited the CUL1 expression on mRNA levels (For HCC1973 cells, the CUL1 level was 0.23HCC19. For MDA-MB-231 cells, the CUL1 level was 0.22 ± 0.04.*P < 0.01 compared with the NC group, which is 1.). b After silencing the CUL1, the TIMP1 level was increased (For HCC1973 cells, the TIMP1 level was 2.81 ± 0.75. For MDA-MB-231 cells, the TIMP1 level was 2.41 ± 0.23.*P < 0.01 compared with the NC group, which is 1.). c The tendency of TRAF2 mRNA expression levels in MDA-MB-231 and HCC-1937 cells were equal to TIMP1 determined by QRT-PCR (For HCC1973 cells, the TRAF2 level was 2.38 ± 0.45. For MDA-MB-231 cells, the TRAF2 level was 2.29 ± 0.33. *P < 0.01 compared with the NC group, which is 1.). d the CUL1, TIMP1 and TRAF2 protein expression levels in HCC-1937 and MDA-MB-231 cells were examined by WB analysis. e After transfected the siRNA-CUL into HCC-1937 and MDA-MB-231 cells, the cell proliferation ratio was inhibited significantly (For HCC1973 cells, the viability ratio was 0.55 ± 0.06. For MDA-MB-231 cells, the viability ratio was 0.53 ± 0.15. *P < 0.01 compared with the NC group, which is 1.). f the Tunnel analysis clarified this negative effect of siRNA-CUL1. g The transwell analysis showed, the numbers of the migrated cells in the NC group of both two TNBC cells, are almost double that are in the siRNA-CUL1 group h. The wound-healing assay showed the cell migration ability was reduced observably in siRNA-CUL1 group. For the NC group, the gap closure rate is more than two to thirds in both HCC-1937 and MDA-MB-231 cells. For siRNA-CUL1 group, the gap closure rate is less than one thirds
