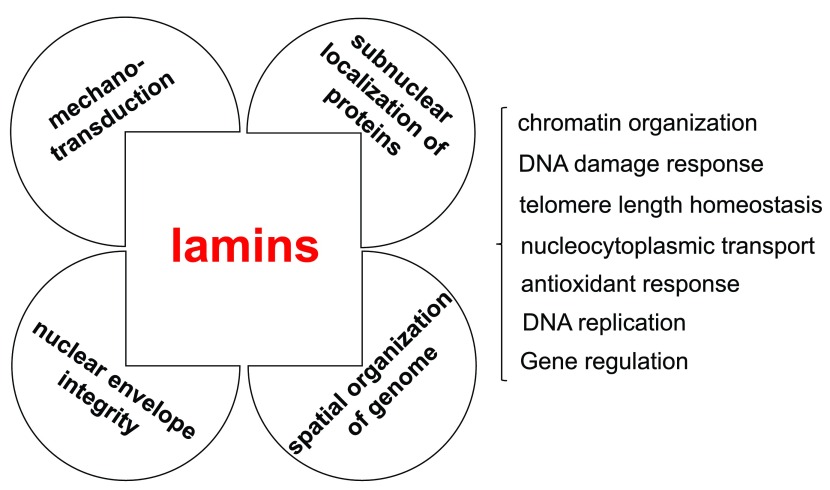
Figure 2. Lamins influence the mechanical properties of the nucleus and contribute to genome organization, function, and stability.
Lamins have roles that support various aspects of nuclear structure and function. Lamins provide mechanical strength to the cell nucleus and contribute to cellular mechanotransduction. Lamins influence the nucleoplasmic environment and contribute to shaping the spatial organization of the genome. Lamins influence genome function and stability by contributing, through interactions with various nuclear factors, to the epigenetic regulation of chromatin, DNA replication and repair, and gene transcription.