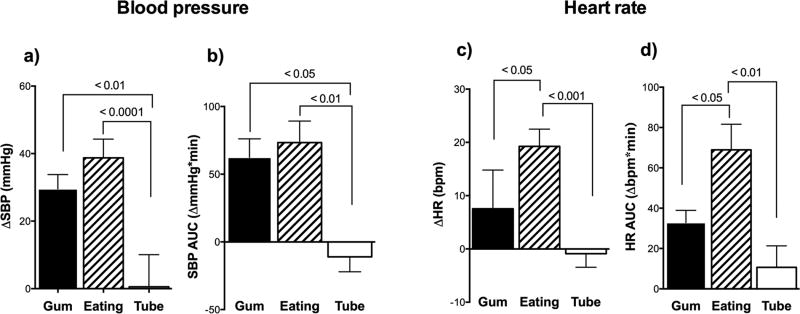
Figure 4. Comparison of responses to chewing, swallowing and stomach distension in patients with familial dysautonomia.
A) Shows significantly greater increase in systolic blood pressure (SBP) when chewing and swallowing compared to when distending the stomach alone during a tube feed. B) Shows area under the curve (AUC) for change in SBP in the first 5 minutes was greater when chewing gum and eating orally compared with feeding directly into the stomach (gastrostomy tube). C) Shows significantly greater increase in heart rate (HR) when eating by mouth compared with chewing gum and gastrostomy feedings. D) Shows area under the curve for change in HR in the first 5 minutes, which was greatest when eating orally. All measurements were taken in the seated position. p-values derived from ANOVA with post-hoc multiple comparisons.