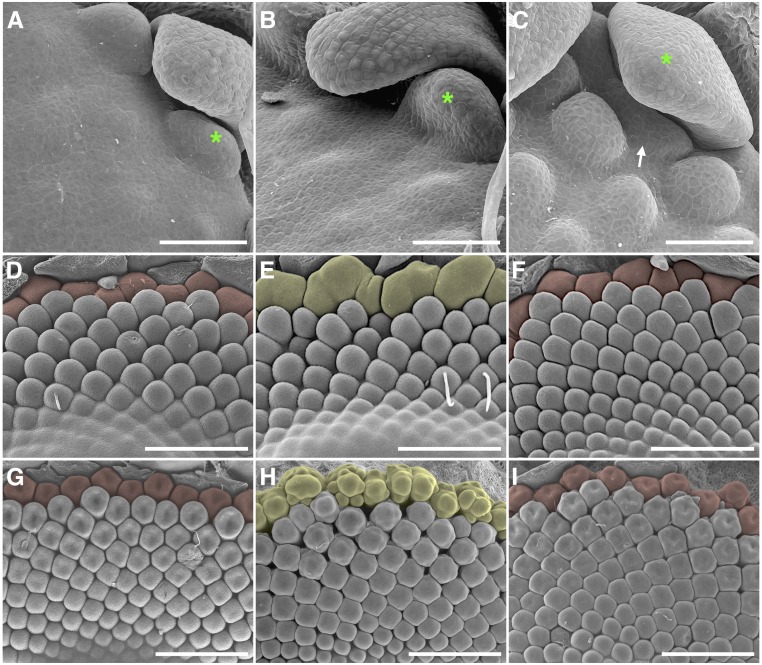
Figure 5.
Early ontogeny of ray primordia initiation in wild-type and transgenic gerbera with suppressed FMI gene functions. A to C, Three consecutive developmental stages of early capitulum development in wild-type gerbera. Trans flowers initiate earlier than ray primordia (arrow) that emerge in the axils of the last series of involucral bracts (green asterisks). D to F, SEM images show that the ray flower initials (shaded in yellow) of GhLFY RNAi plants (E) are distinct from the solitary ray primordia (shaded in red) found in wild-type (D) and GhUFO RNAi (F) plants. G to I, In contrast to wild-type (G) and GhUFO RNAi (I) plants, the marginal ray flower primordia in GhLFY RNAi (H) plants show faster organogenesis compared with nearby trans flower primordia. Bars = 50 µm (A–C) and 500 µm (D–I).