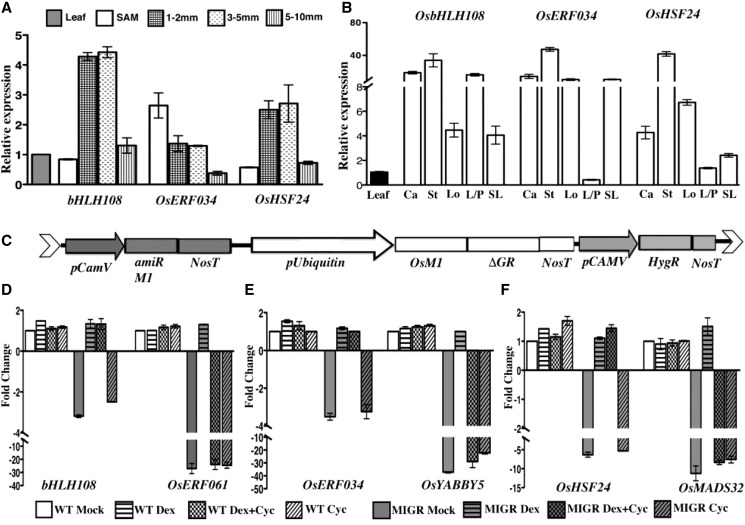
Figure 8.
Expression levels of some OsMADS1 target genes in various floral tissues and their regulation by OsMADS1. A, Relative expression of three direct OsMADS1 target genes—OsbHLH108/SPT, OsERF034, and OsHSF24—in wild-type panicles at different developmental stages. Expression was quantified in tissues of vegetative SAM, with panicles of 1 to 2 mm (branch meristems); 3 to 5 mm (branch meristems, early spikelet, and floral meristem); and 5 to 10 mm (early floral organ differentiation). B, Relative expression of three OsMADS1-bound transcription factor genes in organs of wild-type florets. C, Schematic of the T-DNA segment in the PUbi: OsMADS1-ΔGR; P35S:OsMADS1amiR present in transgenics used for induced complementation studies with OsMADS1-GR. These transgenics were used to study transcriptional regulation of three nodal transcription factor genes and their predicted downstream genes. Wild-type or PUbi: OsMADS1-ΔGR; P35S:OsMADS1amiR (MIGR) plants were subjected to mock, dexamethasone, cycloheximide, or both dexamethasone and cycloheximide simultaneously. D, Quantitation of the fold-change in the normalized expression levels of OsbHLH108 and OsERF061 transcription factor genes in wild-type and MIGR panicles to assess direct and indirect effects of OsMADS1-GR. E, RT-qPCR analyses showing direct transcriptional regulation of OsERF034 by OsMADS1-GR and the indirect regulation of OsYABBY5. F, RT-qPCR analyses showing direct transcriptional regulation of OsHSF24 by OsMADS1-GR and indirect regulation of OsMADS32. Error bars represent se for two biological replicates. Ca, carpel; St, stamen; Lo, lodicule; L/P, lemma/palea; SL, sterile lemma.