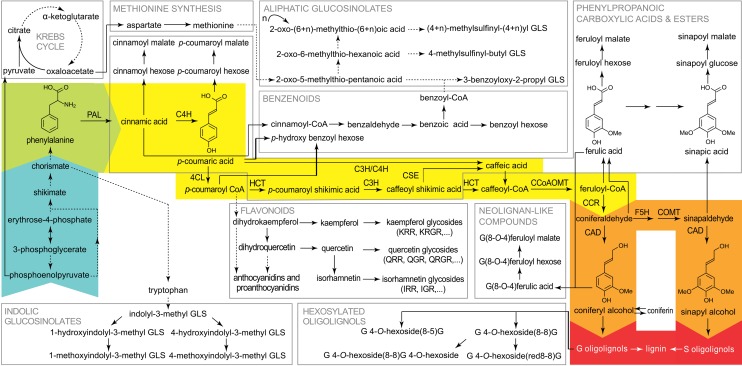
Figure 1.
The phenylpropanoid pathway with a focus on lignin metabolism. Phe (green), derived from the shikimate pathway (blue), is converted via the general phenylpropanoid (yellow) and the monolignol-specific (orange) pathways to the monolignols coniferyl and sinapyl alcohol, which can polymerize into G and S oligolignols (red). Other pathways are intertwined with or branch off from the general phenylpropanoid pathway (in gray squares). Dashed arrows represent multiple enzymatic steps, and solid arrows stand for a single conversion. This figure was adapted from Vanholme et al. (2012b). Proteins: CAD, CINNAMOYL ALCOHOL DEHYDROGENASE; CCoAOMT, CAFFEOYL-COENZYME A O-METHYLTRANSFERASE; CCR, CINNAMOYL-COENZYME A REDUCTASE; C3H, p-COUMARATE 3-HYDROXYLASE; C4H, CINNAMATE 4-HYDROXYLASE; 4CL, 4-COUMARATE:COENZYME A LIGASE; COMT, CAFFEIC ACID O-METHYLTRANSFERASE; CSE, CAFFEOYL SHIKIMATE ESTERASE; F5H, FERULATE 5-HYDROXYLASE; HCT, p-HYDROXYCINNAMOYL-COENZYME A:QUINATE SHIKIMATE p-HYDROXYCINNAMOYLTRANSFERASE; PAL, PHENYLALANINE AMMONIA LYASE. Rhamnosides: GLS, glucosinolate; IGR, isorhamnetin-3-O-glucosyl-7-O-rhamnoside; IRR, isorhamnetin-3-O-rhamnosyl-7-O-rhamnoside; KRGR, kaempferol-3-O-rhamnosyl(1→2)β-glucopyranosyl-7-O-α-rhamnoside; KRR, kaempferol-3-O-rhamnosyl-7-O-rhamnoside; QGR, quercetin-3-O-β-glucopyranosyl-7-O-α-rhamnopyranoside; QRGR, quercetin-3-O-rhamnosyl(1→2)β-glucopyranosyl-7-O-α-rhamnopyranoside; QRR, quercetin-3-O-rhamnosyl-7-O-rhamnoside.