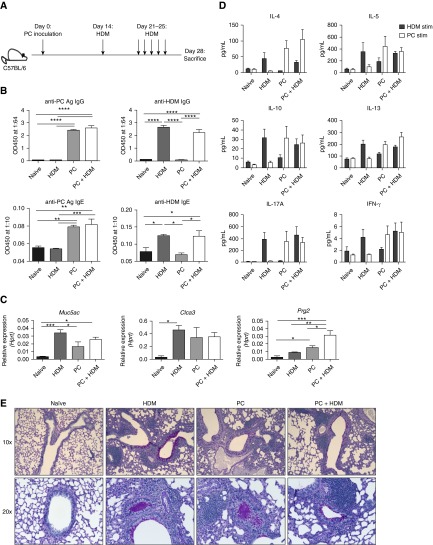
Figure 2.
Pneumocystis (PC) infection and house dust mite (HDM) treatment induce independent type II responses. (A) Mice were untreated (naive), treated with HDM alone, infected with PC alone, or infected with PC and subsequently treated with HDM (n = 4 per group). (B) Infection and HDM treatment generated anti-PC and anti-HDM IgG and IgE antibodies. (C) Increases in type II–associated genes in PC-infected, HDM-treated, and PC- + HDM-treated mice in whole lung as measured by quantitative reverse transcriptase–polymerase chain reaction. (D) Ex vivo cells isolated from whole lung were stimulated with either HDM or PC antigen for 72 hours, and supernatants were analyzed using a Bio-Plex kit. (E) Periodic acid–Schiff staining of naive, HDM-alone, PC-alone mice, as well as mice that received dual treatment, demonstrating increased mucus production following each treatment (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001 by one-way analysis of variance with Tukey’s multiple comparisons). Ag = antigen; Hprt = hypoxanthine phosphoribosyltransferase; OD450 = optical density at 450 nm.