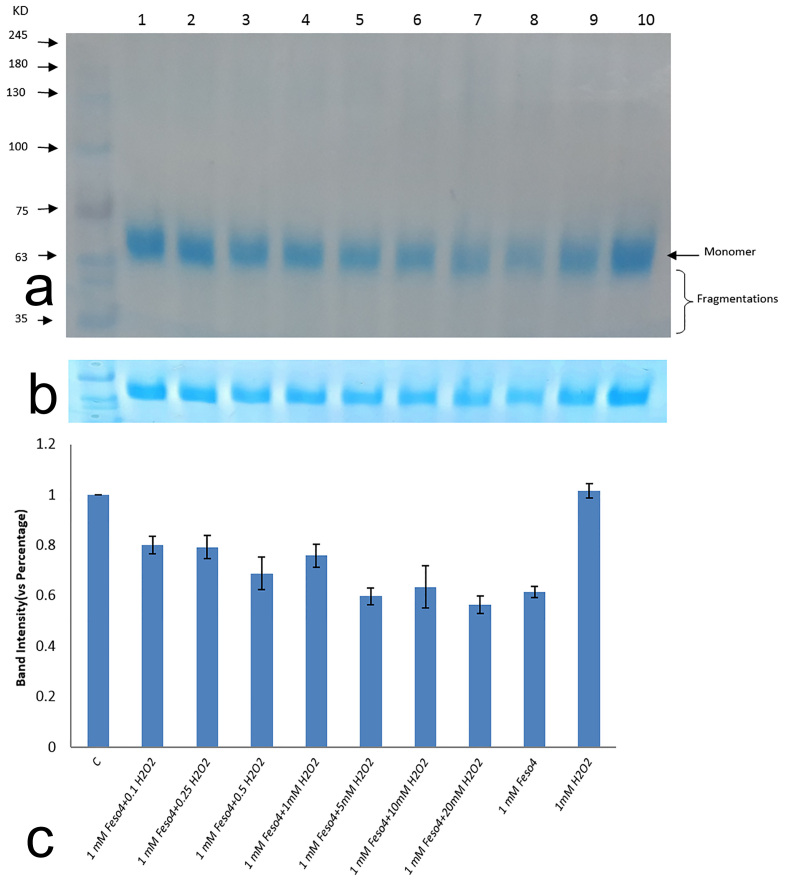
Figure 1.
HSA oxidation as a function of Fenton reaction in different ratios. A) HSA was oxidized by increasing ratio of H2O2 to FeSo4 and analyzed by SDS-PAGE (10% Poly acrylamide). Lane 1: control group, Lane 2: H2O2 (0.1mM) + FeSo4 (1mM); Lane 3: H2O2 (0.25mM) + FeSo4 (1mM); Lane 4: H2O2 (0.5mM) + FeSo4 (1mM); Lane 5: H2O2 (1mM) + FeSo4 (1mM), Lane 6: H2O2 (5mM) + FeSo4 (1mM), Lane 7: H2O2 (10mM) + FeSo4 (1mM), Lane 8: H2O2 (20mM) + FeSo4 (1mM), Lane 9: FeSo4 (1mM), Lane 10: H2O2 (1mM). B) SDS-PAGE profile of HSA disappearance treated with different ratios of Fenton reaction. C) The average percentage of band intensity of HSA (4μg) as a function of Fenton reaction in different levels. Calculations were performed to similarly treated samples from triplicate experiments