Figure 3.
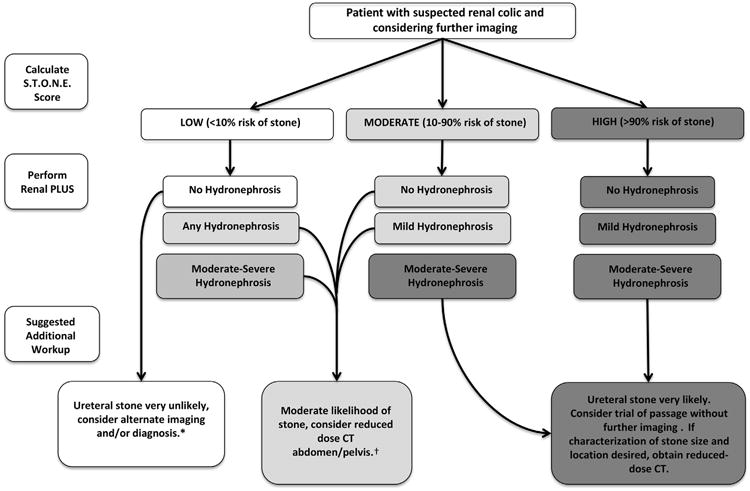
Suggested algorithm incorporating STONE score for symptomatic stone and renal PLUS for diagnosis and management of ED patients with suspected renal colic. Moderate-risk patients with moderate hydronephrosis may be managed similarly to high-risk patients. Renal PLUS does not significantly add to diagnosis of symptomatic stone in high-risk patients, but the absence of hydronephrosis makes the need for urologic intervention unlikely. *Approximately three quarters of CT scans in the low-risk group were nondiagnostic. †Approximately two thirds of low-risk patients with moderate hydronephrosis or moderate-risk patients with any hydronephrosis will have a symptomatic stone. Low- and moderate-risk patients with hydronephrosis are at increased risk of subsequent need of urologic intervention.
