FIGURE 4.
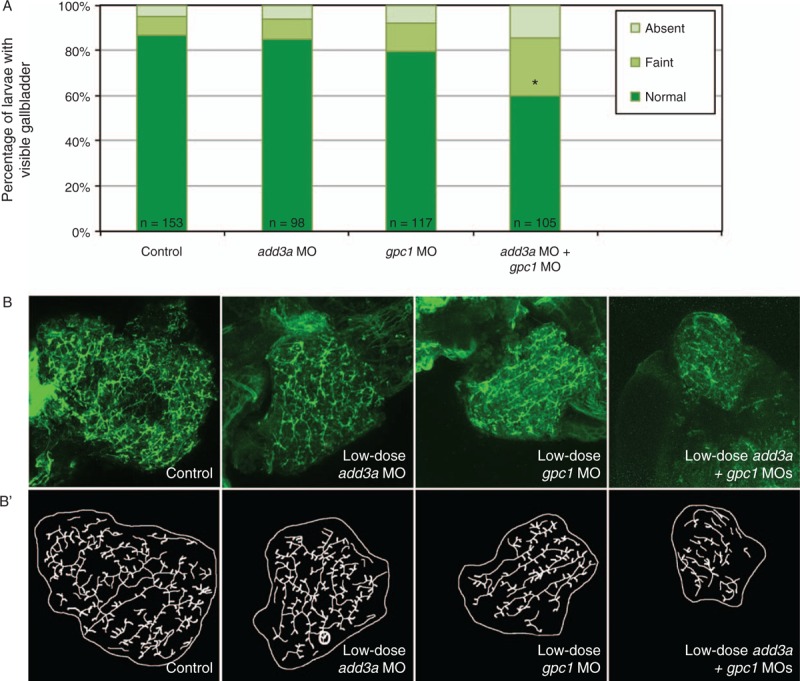
Epistatic effect of coinjection of add3a and gpc1 morpholinos on biliary function and development. Wild-type fertilized oocytes were injected with MO directed against add3a or gpc1 at lower amounts needed to see an effect, or control. At 5 days post fertilization (dpf), larvae were incubated in the fluorescent lipid PED6 and assayed for gallbladder uptake, and then fixed and stained for cytokeratin to document biliary anatomy. A, Percentages of control (cont), low-dose add3a MO-injected, low-dose gpc1 MO-injected, or add3a and gpc1 MO-injected larvae with normal, faint, or absent gallbladder visibility, reflecting PED6 uptake and thus biliary function. There is a significant decrease in biliary function only in the larvae injected with the lower dose of both MOs (∗P ≤ 0.0001 by chi-square analysis). B, Confocal projections of cytokeratin immunostainings of livers from 5 dpf larvae injected with control (cont), low-dose add3a MO, low-dose gpc1 MO, or the combination of both MOs at the lower dose. B’, Schematics of the respective panels shown in (B). Note that the intrahepatic duct pattern is similar in the control and the larvae injected with add3a or gpc1 MO alone, but that when the MOs are injected together the pattern is abnormal, with decreased duct density and complexity. Original magnification ×400. MO = morpholino antisense oligonucleotide.
