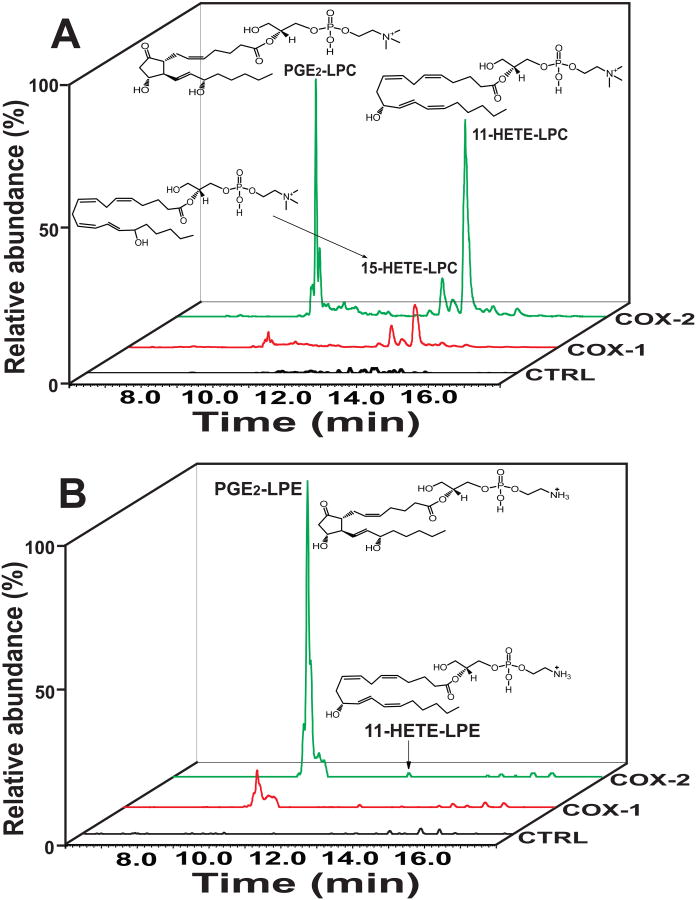
Figure 1. Cyclooxygenases mediate oxidation of 2-arachidonoyl-lysolipids (2-AA-LPC and 2-AA-LPE) to produce novel eicosanoid-lysolipids.
Extracted ion chromatograms of COX-1 and COX-2 oxidized eicosanoid-lysolipid products utilizing either 2-AA-LPC (A) or 2-AA-LPE (B) as substrate. Purified recombinant COX-1 (2 μg) or COX-2 (2 μg) was incubated with 2-AA-LPC (10 μM) or 2-AA-LPE (10 μM) in 100 mM Tris-HCl buffer (pH 8.0) at 30°C for 10 min. The reaction was terminated by addition of methanol and acidified to pH 4 with glacial acetic acid. The reaction products were then purified by solid phase extraction following separation on a C18 HPLC column prior to analysis utilizing an LTQ-Orbitrap mass spectrometer with a mass resolution of 30,000 at m/z=400 in the positive ion mode. The extracted ion chromatograms (with 3 ppm mass window) for the identified metabolic products of PGE2-LPC (m/z 592.3245), 11-HETE-LPC (m/z 560.3347), and 15-HETE-LPC (m/z 560.3347) for 2-AA-LPC as well as PGE2-LPE (m/z 550.2726) and 11-HETE-LPE (m/z 518.2877) for 2-AA-LPE are shown.