Figure 4. Eicosanoid-lysolipids present in wild-type (WT) and iPLA2γ-/-(KO) murine hepatic tissue.
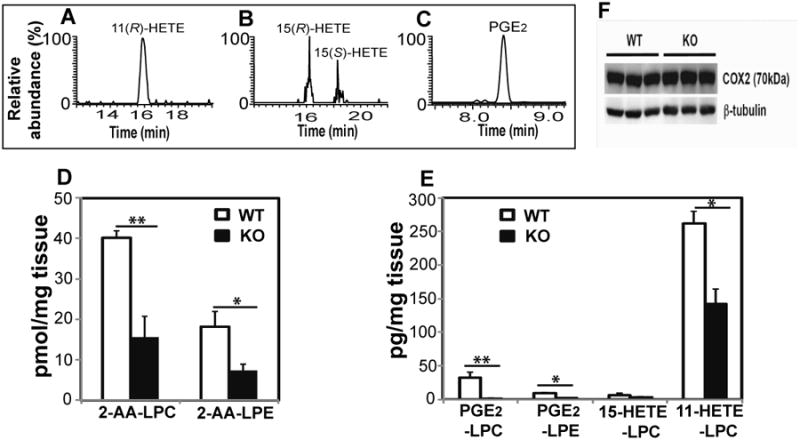
Hepatic tissue was isolated from wild-type (WT) and iPLA2γ knock-out (KO) mice and flash frozen in liquid nitrogen. The extracts were purified by solid-phase extraction and the isolated eicosanoid-lysolipids were hydrolyzed by purified recombinant cPLA2α followed by charge-switch derivatization with AMPP, chiral chromatographic separation, and compared with authentic stereospecific standards. A-C, Stereochemical determination of eicosanoid-lysolipid products present in WT hepatic tissue; D, Content of 2-AA-LPC and 2-AA-LPE in hepatic tissue from WT and KO mice; E, Content of PGE2-LPC, PGE2-LPE, 11-HETE-LPC, and 15-HETE-LPC in hepatic tissue from WT and KO mice. Data are expressed as mean values ± SEM of six replicates. Statistical analyses were performed using an unpaired two-tailed Student t test; P<0.05 was considered significant. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01; F, Western analysis of COX-2 expression in WT and KO mouse liver using β-tubulin as a loading control.
