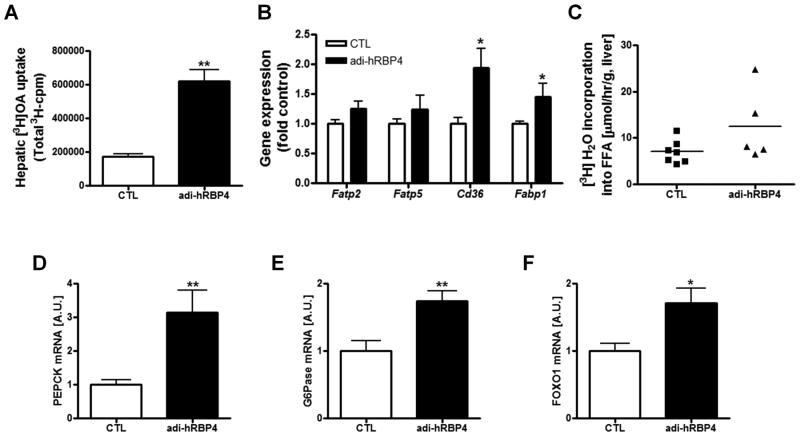
Figure 5. Fatty acid uptake contributes to hepatic steatosis in adi-hRBP4 mice fed a high-fat diet and hepatic gluconeogenic genes are markedly increased.
(A) FFA uptake into the livers of matched adi-RBP4 and littermate control mice was quantified by assessing 3H-cpm (n = 3 - 6) 5 minutes after an iv injection of [3H]oleic acid. (B) mRNA expression of genes related to FFA uptake in liver as determined by qPCR (n = 4 - 6). (C) The rate of hepatic de novo lipogenesis for matched high-fat fed adi-RBP4 and littermate control mice as quantified by measuring [3H]H2O incorporated into lipid (n = 6 - 7). mRNA levels of the key hepatic gluconeogenic genes Pepck (D) and G6Pase (E) as well as Foxo1 (F) were determined for liver by qPCR (n = 4 - 6) for matched high-fat diet fed adi-hRBP4 and littermate controls. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 versus controls (CTL). AU, Arbitrary units. Data are expressed as means ± SEM.