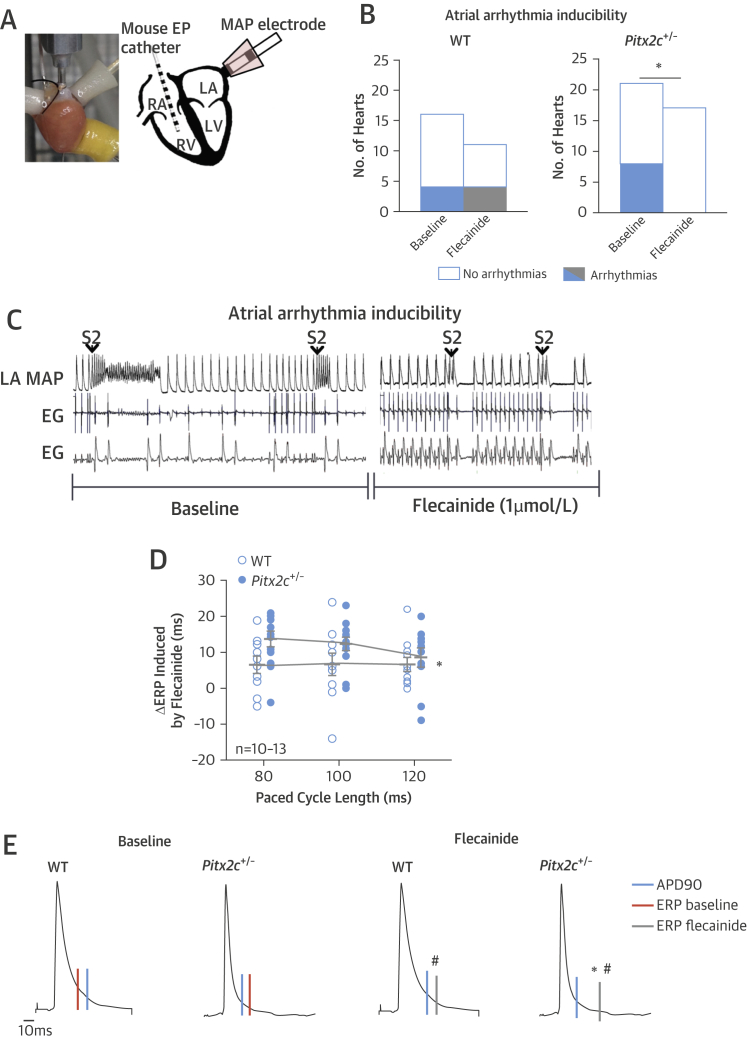
Figure 1.
Atrial Arrhythmia Inducibility in Pitx2c+/– Murine Whole Hearts
(A) Image and schematic representation of the Langendorff-perfused heart. (B) Atrial arrhythmia inducibility in isolated, beating hearts from wild-type (WT) and reduced paired like homeodomain 2 messenger ribonucleic acid (Pitx2c+/–) mice. Flecainide abolished atrial arrhythmia inducibility in Pitx2c+/– hearts only. *p < 0.05 flecainide versus baseline. (C) Representative trace of atrial fibrillation (AF) induced during programmed stimulation at baseline, showing reduced severity of arrhythmias with 1 μmol/l flecainide in Pitx2c+/– atria. (D) Effects of flecainide on atrial effective refractory period (ERP) in wild-type and Pitx2c+/– isolated, beating hearts. Shown is the difference in atrial ERP between baseline and 1 μmol/l flecainide at 80- to 120-ms paced cycle length following a single extrastimulus (S2) in WT and Pitx2c+/– isolated, beating hearts. *p < 0.05 between genotypes across all cycle lengths. (E) Whereas flecainide prolonged ERP in both genotypes, this effect was more pronounced in Pitx2c+/– atria. Flecainide caused post-repolarization refractoriness (PRR), the difference between ERP (orange and grey lines) and APD90(blue lines), in WT and Pitx2c+/– atria. Flecainide-induced PRR in Pitx2c+/– is almost 3 times that of WT atria. *p < 0.05 WT versus Pitx2c+/–. #p < 0.05 baseline versus 1 μmol/l flecainide. APD = action potential duration; EG = intracardiac electrogram; EP = electrophysiology; LA = left atrium; LV = left ventricle; MAP = monophasic action potential; RA = right atrium; RV = right ventricle.