Fig. 4.
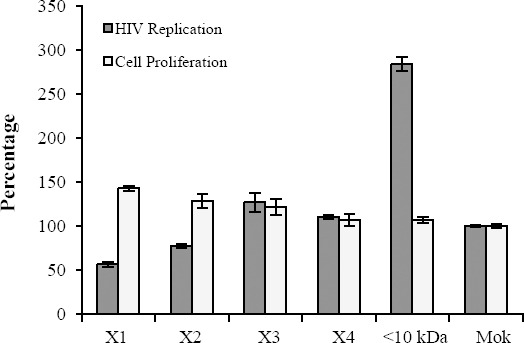
Anti-HIV activity of various fractions of H. lepturus venom. One of the extracted phospholipases (X1) showed the most anti-HIV activity among fractions extracted from crude venom. It inhibited about 43.5% of replication at 20 µg/ml concentration. The H. lepturus venome also encompassed a fraction of small peptides (>10 kDa) with considerable activity for facilitating HIV replication.
