Figure 1.
Metabolic and Proteomic Profiling Reveals Distinct Changes in L-Arginine Metabolism in Activated Human T Cells
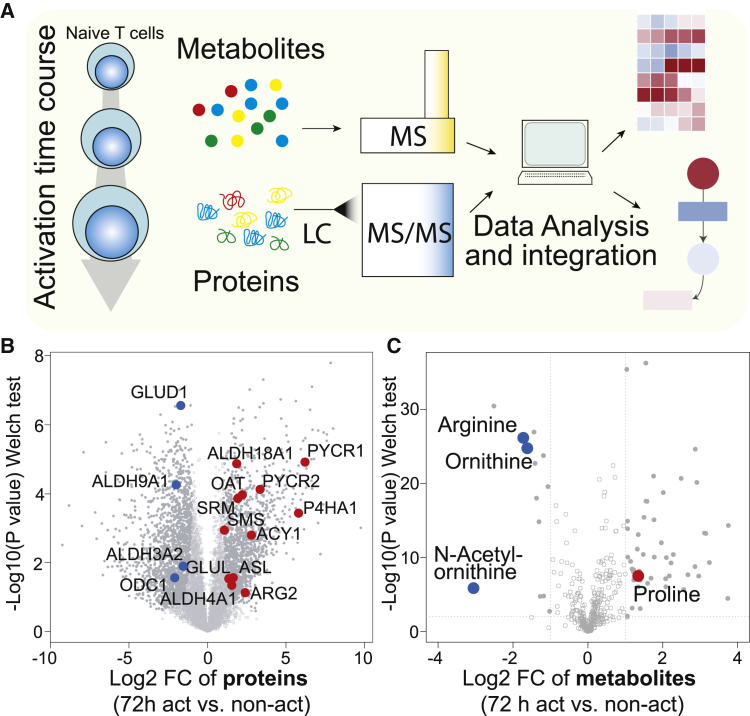
(A) Schematic view of the experimental approach.
(B) Comparison of protein abundances between 72-hr-activated (CD3 + CD28 antibodies) and freshly isolated non-activated human naive CD4+ T cells. Closed circles indicate proteins that changed significantly (FDR = 0.05, S0 = 1). Colored dots are enzymes of the arginine and proline metabolism that changed significantly.
(C) Comparison of metabolite abundances in 72 hr-activated and freshly isolated non-activated human naive CD4+ T cells. Closed circles indicate metabolites that changed significantly (|Log2 fc| > 1, p < 0.01). Colored dots are metabolites of the arginine and proline metabolism that changed significantly. Similar changes were observed when 72 hr-activated CD4+ T cells were compared with naive CD4+ T cells cultured overnight in the absence of TCR stimulation.