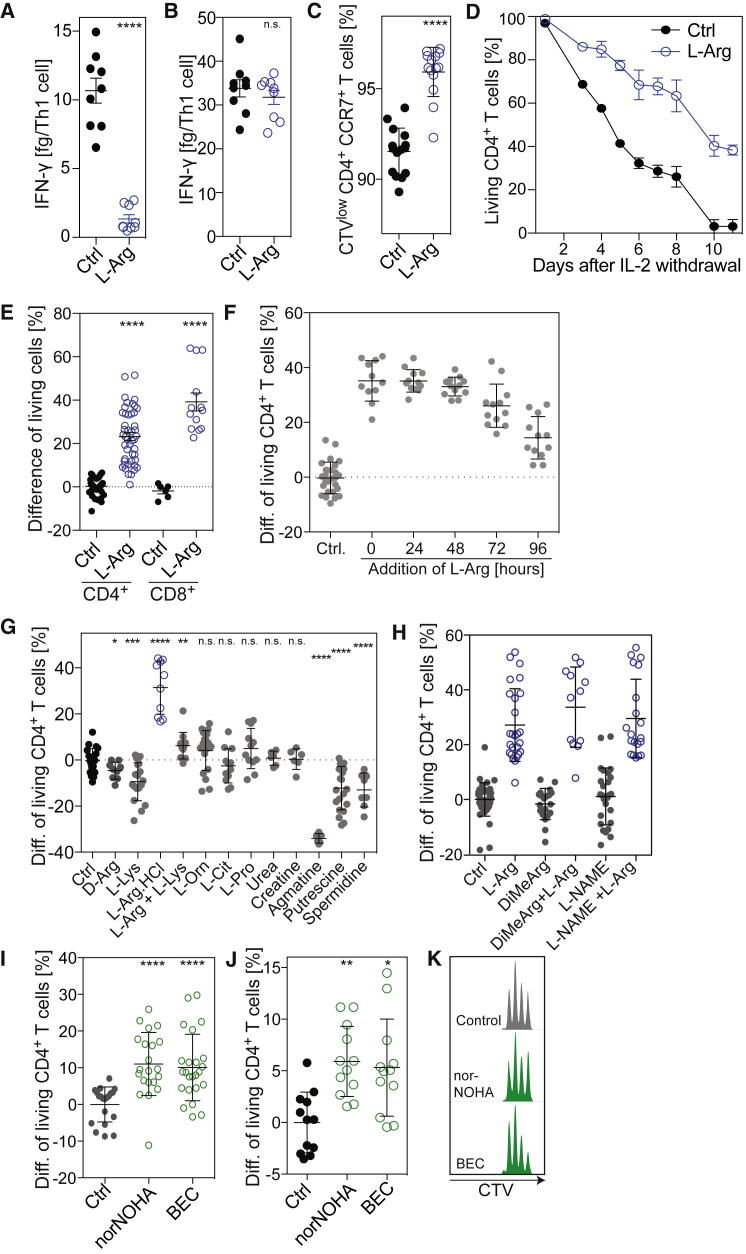
Figure 4.
L-Arginine Limits Human T Cell Differentiation and Endows Cells with a High Survival Capacity In Vitro
(A and B) Human naive CD4+ T cells were activated in L-Arg medium or Ctrl medium in the presence of 10 ng/mL IL-12. IFN-γ was quantified in culture supernatants after 5 days (A) or after re-activation for 5 hr with PMA/ionomycin (B); n = 9 from three donors.
(C) Naive CD4+ T cells were labeled with CellTrace Violet (CTV) and activated in L-Arg medium or Ctrl medium. On day 10, proliferating CTVlo T cells were stained with an antibody to CCR7 and analyzed by flow cytometry; n = 15 from three donors.
(D) Naive CD4+ T cells were activated for 5 days in L-Arg or Ctrl medium in the presence of exogenous IL-2, washed extensively, and cultured in Ctrl medium in the absence of IL-2. Shown is the percentage of living T cells as determined by Annexin V staining at different time points after IL-2 withdrawal. One representative experiment out of three performed.
(E) Same experiment as in (D). Shown is the difference of living activated CD4+ and CD8+ T cells 5 days after withdrawal of IL-2; n = 46, from 16 donors (CD4+ T cells); n = 13, from four donors (CD8+ T cells).
(F) Difference of living activated CD4+ T cells 5 days after IL-2 withdrawal. Naive CD4+ T cells were activated and L-Arg (3 mM) was added to the culture medium at the indicated time points; n = 12 from four donors.
(G) Difference of living activated CD4+ T cells 5 days after IL-2 withdrawal. Naive CD4+ T cells were activated in Ctrl medium or medium supplemented with the indicated metabolites (3 mM, except for spermidine 0.1 mM). Ctrl, n = 21; D-Arg, n = 9; L-lysine, n = 18; L-Arg-HCl, n = 10; L-Arg + L-Lys, n = 12; L-Orn, n = 20; L-Cit, L-Pro, n = 12; urea, creatine, agmatine, n = 6; putrescine, n = 18; spermidine, n = 8, from at least three donors.
(H) Difference of living activated CD4+ T cells 5 days after IL-2 withdrawal. Naive CD4+ T cells were activated in the presence or absence of nitric oxide synthase inhibitors dimethylarginine (DiMeArg) or L-NG-nitroarginine methyl ester (L-NAME), both used at 1 mM. Ctrl and L-Arg, n = 26; DiMeArg and L-NAME, n = 16; DiMeArg + L-Arg and L-NAME + L-Arg, n = 12, from at least three donors.
(I) Difference of living activated CD4+ T cells 5 days after IL-2 withdrawal. Naive CD4+ T cells were activated in absence (Ctrl) or presence of the arginase inhibitors Nω-Hydroxy-nor-L-arginine (norNOHA, 300 μM) or S-(2-boronoethyl)-L-cysteine (BEC, 300 μM); n = 21, from seven donors.
(J) Same as in (I) but cultures were performed in medium containing 150 μM L-arginine.
(K) Effect of norNOHA and BEC on proliferation of CTV-labeled naive T cells measured 72 hr after activation. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001, ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001 (Student’s t test).
(A–J) Error bars represent SEM throughout.
See also Figures S3 and S4.