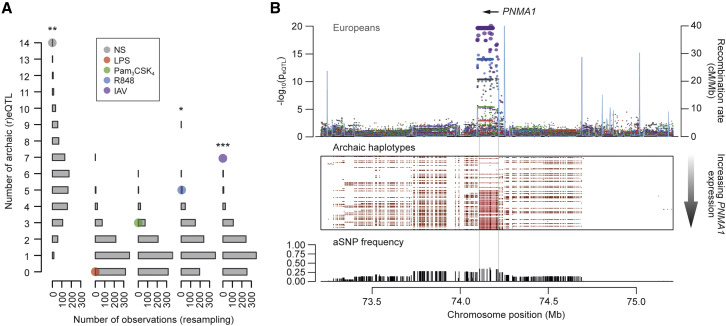
Figure 6.
Neandertal Introgression of Immune Regulatory Variants in Europeans
(A) Enrichment of (r)eQTLs in archaic SNPs. The observed number of archaic eQTLs is presented for each condition (colored dots) in Europeans with respect to the expected distribution of archaic eQTLs under the assumption of independence (gray bars) (see STAR Methods) (∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001).
(B) Fine mapping of the archaic reQTL at PNMA1 in Europeans. SNP associations with PNMA1 expression (−log10(peQTL)) for the basal (gray) and stimulated (in colors) conditions (top). European individuals, and their corresponding archaic and modern haplotypes at the PNMA1 locus, are sorted by increasing levels of PNMA1 expression. Red dots represent archaic SNPs, and red lines represent the largest consecutive stretch of archaic alleles associated with PNMA1 expression (middle). Frequency distribution of archaic SNPs at the locus is shown (bottom). Only the gene for which the eQTL was observed is represented.