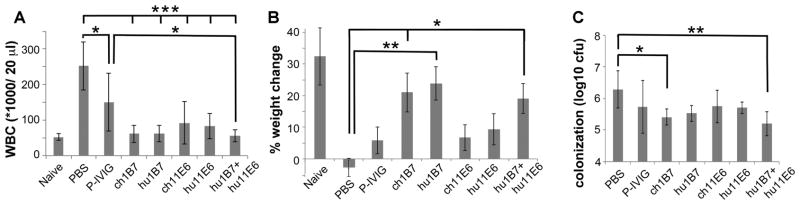
Figure 4. Prophylactic treatment with humanized antibodies protects mice against pertussis.
Mice (n=6) were each administered 20 μg antibody intraperitoneally two hours before infection with 5×106 cfu B. pertussis D420 bacteria. The infection severity was assessed on day 10 by A, CD45+ leukocyte count (WBC), B, weight gain and C, bacterial colonization of the lungs. No bacteria were recovered from uninfected animals. Means ± standard error are shown; significance * p<0.05, ** p<0.01 and *** p< 0.001 versus PBS-treatment is indicated, using Tukey’s simultaneous test. Additionally, only P-IVIG-treated mice had WBC distinguishable from uninfected naïve mice (p<0.01) and mice treated with hu1B7, ch1B7 or the antibody cocktail had lower WBC than P-IVIG-treatment for equivalent doses (p<0.05). Only mice treated with P-IVIG and ch11E6 exhibited reduced weight gain relative to uninfected mice (p<0.05).