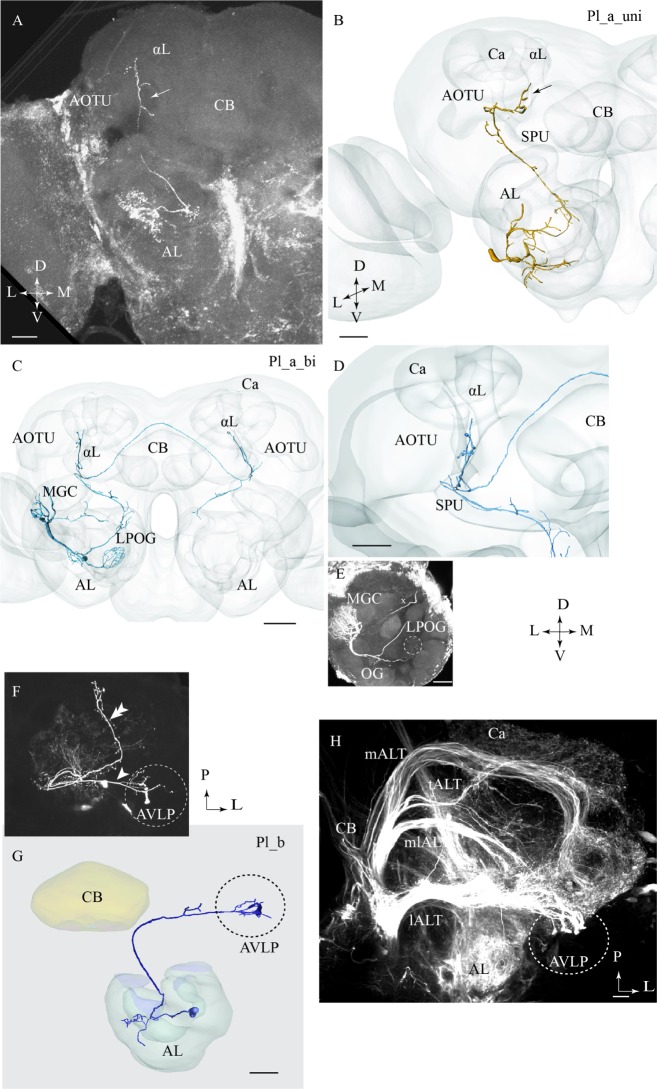
FIGURE 3.
Three different sub-categories of lateral-tract neurons, named Pl_a_uni, Pl_a_bi, and Pl_b, presented by means of confocal images and 3D reconstructions. (A) and (B) The Pl_a_uni neuron follows the initial dorso-lateral course of the lateral antennal-lobe tract, but then, at the spur (SPU) of the mushroom bodies, it bends off from this path and continues dorsally terminating in a region between the anterior optic tubercle (AOTU) and the alpha-lobe (αL), the so-called column (arrow). (C–E) The Pl_a_bi neuron displays a projection pattern comparable to that of the aforementioned neuron by terminating in the column. This bilateral neuron sends off a projection to the contralateral hemisphere, targeting a region symmetrical to that described above. Among the glomeruli innervated in the ipsilateral AL, is the cumulus of the macro glomerular complex (MGC) and the labial pit organ glomerulus (LPOG). (F–H) The third neuron category, named Pl_b, projects directly to the AVLP. Here, it extends a few relatively short processes, one of which ends up in a prominent club-like structure. The Pl_b neuron in (F), indicated by an arrowhead, was stained simultaneously with a Pl_a_uni neuron (double arrowhead). The 3D reconstruction in (G) presents the distinct morphology of the individual Pl_b neuron. The confocal image in (H) shows mass-stained antennal-lobe projection neurons (PNs) including a population of approximately 10 lateral-tract neurons possessing a characteristic terminal ending in the AVLP, identical to the club-like structure mentioned above (indicated by the dashed circle). Ca, calyces; L, lateral; P, posterior; M, medial; A, anterior. Scale bars = 50 μm.