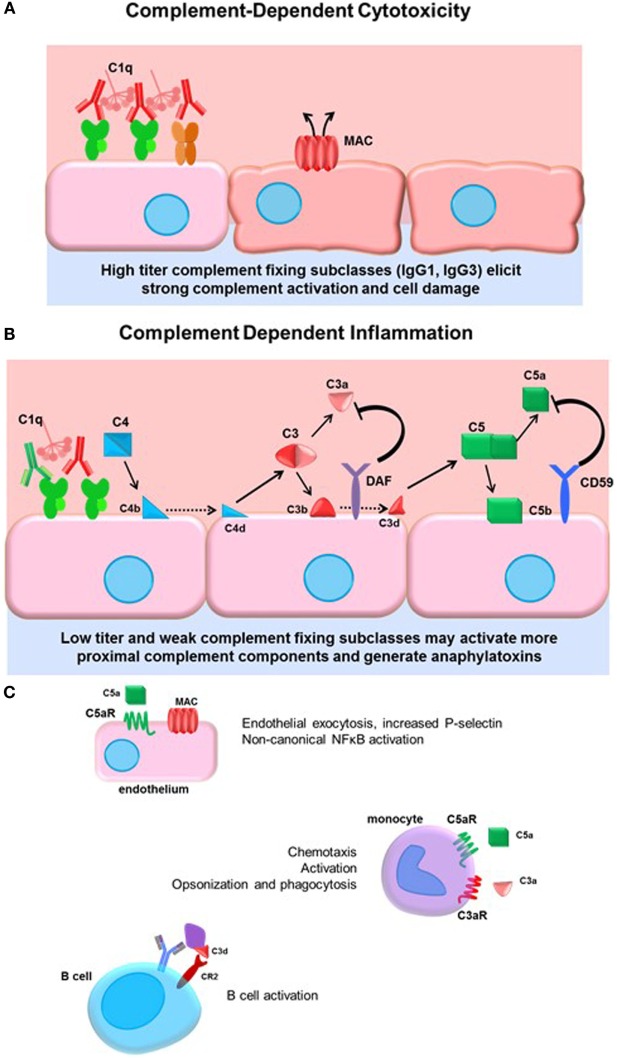
Figure 2.
Complement-dependent cytotoxicity and inflammation. (A) High titers of antidonor HLA antibodies, particularly of the efficient complement-fixing subclasses IgG1 and IgG3, may promote terminal classical complement pathway activation. Complement activation must overcome the regulatory factors and push complement activation to terminal MAC formation and cell damage. (B) Lower titers of antibody or less efficient complement-fixing subclasses, such as IgG2, may result in truncated complement activation, with upstream anaphylatoxin release and opsonin deposition. The initiator C1 complex, composed of globular C1q, embedded with catalytically active C1r and C1s, recognizes the Fc portion of IgM and most of the IgG subclasses, triggering a conformational change in the hexameric shape of the C1 complex. This activates the autocatalytic cleavage of C1r, which then activates C1s. C4 and C2 are cleaved by C1s, forming C4a and C2a split products that generate the C3 convertase. C3 convertase cleaves C3 protein into C3a, a soluble inflammatory protein, and C3b, which is covalently bound to the cell surface. C3b may be further cleaved to C3d or form the C5 convertase. Terminal activation of the C5 convertase cleaves C5 protein, generating the potent anaphylatoxin C5a and the membrane-bound C5b. C5b recruits C6–9 proteins to form the membrane attack complex (MAC), disrupting membrane integrity. Complement regulatory proteins DAF and CD59 at the host cell surface restrain activation of the complement cascade at the two key amplification steps, C3 cleavage and C5 cleavage. (C) Many cells express receptors for the soluble and membrane-bound complement split products. Endothelial cells respond to C5a by upregulating P-selectin, and to sublytic concentrations of MAC by activation of non-canonical NFκB pathways, adhesion molecule, and cytokine upregulation. Monocytes and neutrophils express C3a and C5a receptors, which participate in chemotaxis of myeloid cells. Complement receptor 2 (CR2) is a component of the BCR that binds to opsonized, C3d-coated antigen. CR2 signaling enhances the BCR signal and lowers the threshold for B cell activation.