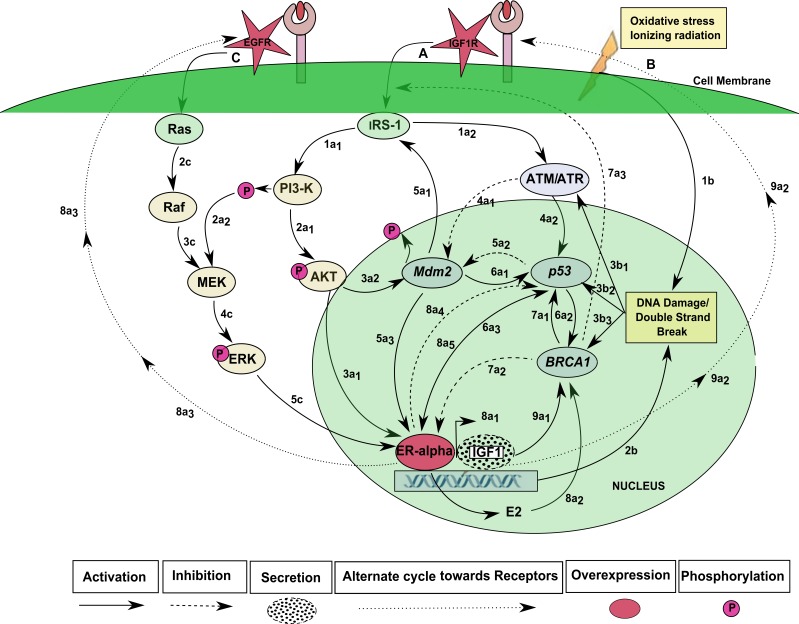
Figure 1. IGF-1R and EGFR signaling pathway.
(A) Ligand activated Insulin growth factor receptor-1 (IGF-1R) signaling starts from the membrane to induce the insulin receptor-1 signaling. IRS-1 down-regulates the phosphoinositide-3 kinase (PI3-K) (1a1) which phosphorylates protein kinase B (AKT) (2a1). IRS-1 signaling further activates the downstream mediator Ataxia telangiectasia mutated Rad3-related (ATM/ATR) protein (1a2). Phosphorylated serine/threonine protein kinase (AKT) and Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase (ERK) signaling enhance the transactivation of estrogen receptor-alpha (ER-α) gene (3a1, 5c) which up-regulates the expression of insulin like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) (8a1). ER-α activates the p53 (8a5) BRCA1 gene indirectly by stimulation of estrogen (E2) in breast cells (8a2) and also respond to the activation of p53 gene (6a3). The role of ER-α in E2-independent manner and secreted IGF-1 mediates the over-expression of IGF-1R (9a2). An important role of TSG (BRCA1) also activates by the gene p53 (6a2). BRCA1 suppresses the levels of ER-α (7a2) have the ability to induce apoptosis rather than cell proliferation. BRCA1 gene can also inhibit the phosphorylation of signaling pathways of IGF-1 receptor (7a3). p53 also activates by BRCA1 (7a1) which regulates the activation of Mdm2 (6a1) that also suppress the over-activation of p53 (5a2). (B) There are some mutations due to radiation or oxidative stress that leads to the phosphorylation of ATM/ATR genes (1b, 3b1, 3b2, 3b3) and DNA damage response occurs through the increased expression of ER-α gene (2b) which inhibits the expression of p53 (8a4). Phosphorylated Mdm2 expression leads to cell cycle proliferation (5a1) by the activation of mutated ATM/ATR signaling cascades (4a1). (C) An alternate pathway of ER-α signaling with estradiol may also utilize epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) for signal transduction, which may further activate the Ras, Raf protein kinases (2c, 3c). E2 causes phosphorylation of PI3-Kinase which stimulates the MEK kinase (2a2) and enhances the activation of extracellular-regulated kinase (ERK) (4c). In breast cancer (BC) cells the expression levels of ER-α is increased by phosphorylation of two receptors, IGF-1R and EGFR (8a3, 9a2).