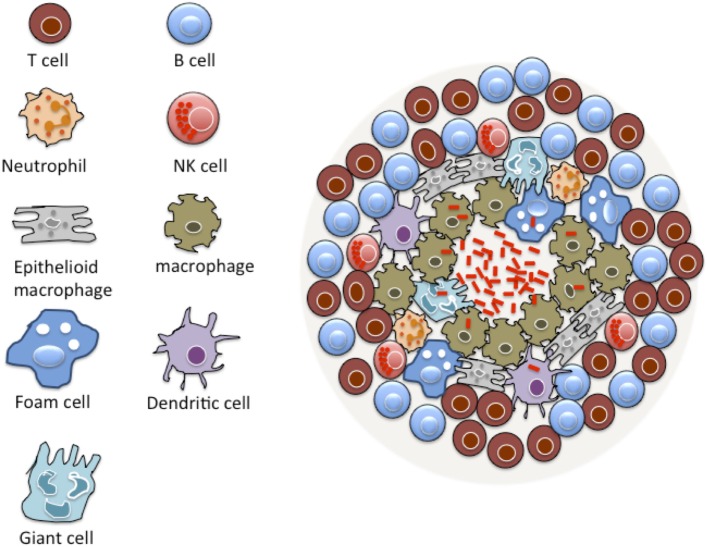
Figure 1.
Basic structure of TB granuloma. A granuloma is a compact immunological structure rich with macrophages at the center. Macrophages can undergo specialized transformation differentiating into other cell types, such as epithelioid cells, multi-nucleated giant cells, and foamy macrophages that are accumulated with lipid droplets. A lymphocytic cuff that is largely comprised of B and T cells characterizes the periphery of the granuloma. Many other cell types are known to constitute a granuloma, including neutrophils, dendritic cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and fibroblasts.