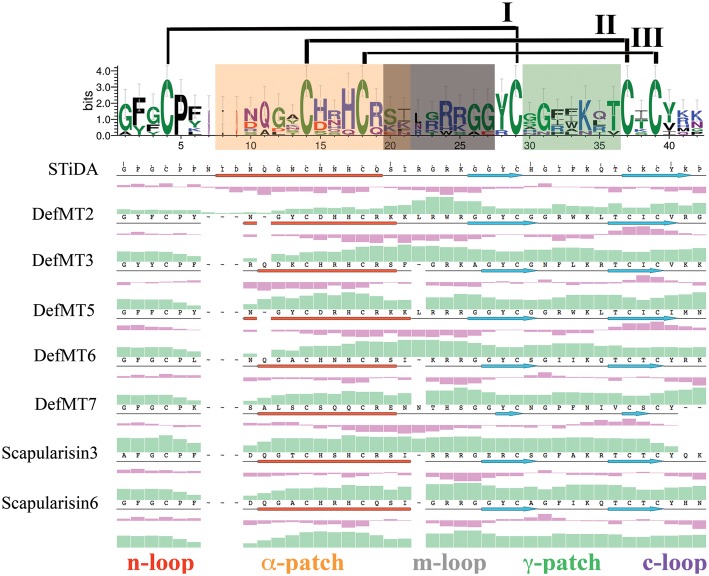
FIGURE 4.
Sequence-based physicochemical properties of STiDA and extant tick defensins. The logo above the multiple sequence alignment demonstrates indels and mutations between STiDA and extant tick defensins. The overall height of the stack indicates the sequence conservation, the height of each residue is it relative frequency, and the width of each residue is proportional to its validity, e.g., thin residues have many gaps. The colors indicate the chemical properties of each residue: green = polar; purple = neutral; blue = basic; red = acidic; black = hydrophobic. The error bars are based on a Bayesian 95% confidence interval. The disulfide bridges are noted and ordered in roman numerals. The motifs described by Tian et al. (2008) responsible for antimicrobial/fungicidal activity are equally color-coded throughout the figure and labeled as α-patch (within the α-helix; orange), the m-loop (the α-helix/β-sheet loop; gray), and the γ-patch (theβ-hairpin loop; green). The position of the α-helices (depicted as red cylinders) and β-sheets (depicted as blue arrows) are shown below the amino acid sequence of each defensin. The n-loop (red) and c-loop (purple) denote the N- and C-terminus, respectively. The secondary structure, hydrophobicity (purple histograms) and isoelectric points (green histograms) are plotted below each sequence of the alignment.