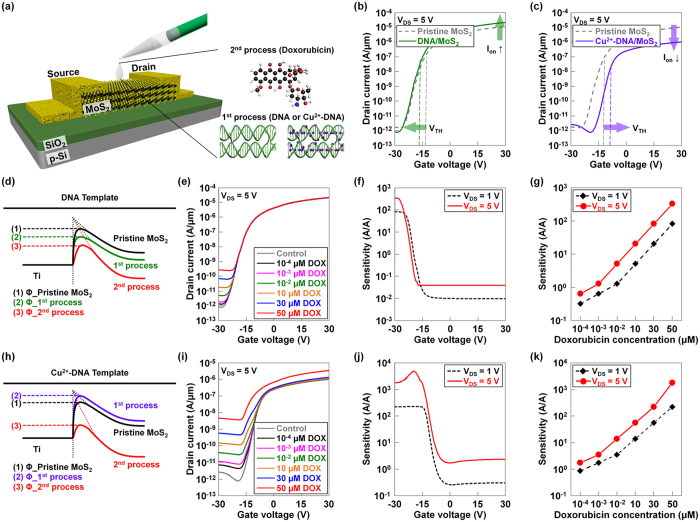
Figure 3. Characterization of DNA/MoS2- and Cu2+-DNA/MoS2-based bio-FETs.
(a) Schematic diagrams of back-gate type FETs, and the process of detecting doxorubicin molecules. ID-VG characteristics of MoS2 bio-FETs before and after coating the (b) DNA or (c) Cu2+-DNA nanostructures. The energy band diagrams at Ti/MoS2 junctions of (d) pristine MoS2, DNA/MoS2 (1st process), and DNA/MoS2 after detecting doxorubicin (2nd process) and (h) pristine MoS2, Cu2+-DNA/MoS2 (1st process), and Cu2+-DNA/MoS2 after detecting doxorubicin (2nd process). ID-VG characteristics of (e) DNA/MoS2- and (i) Cu2+-DNA/MoS2-based bio-FETs according to various concentrations of doxorubicin (10−4 μM, 10−3 μM, 10−2 μM, 10 μM, 30 μM, and 50 μM). Calculated sensitivity ((Ioff_after sensing − Ioff_before sensing)/Ioff_before sensing) of (f) DNA/MoS2- and (j) Cu2+-DNA/MoS2-based bio-FETs as a function of gate voltage at different drain voltages when detecting 50 mM of doxorubicin. The sensitivity of (g) DNA/MoS2- and (k) Cu2+-DNA/MoS2-based bio-FETs as a function of the concentration of doxorubicin at different drain voltages.