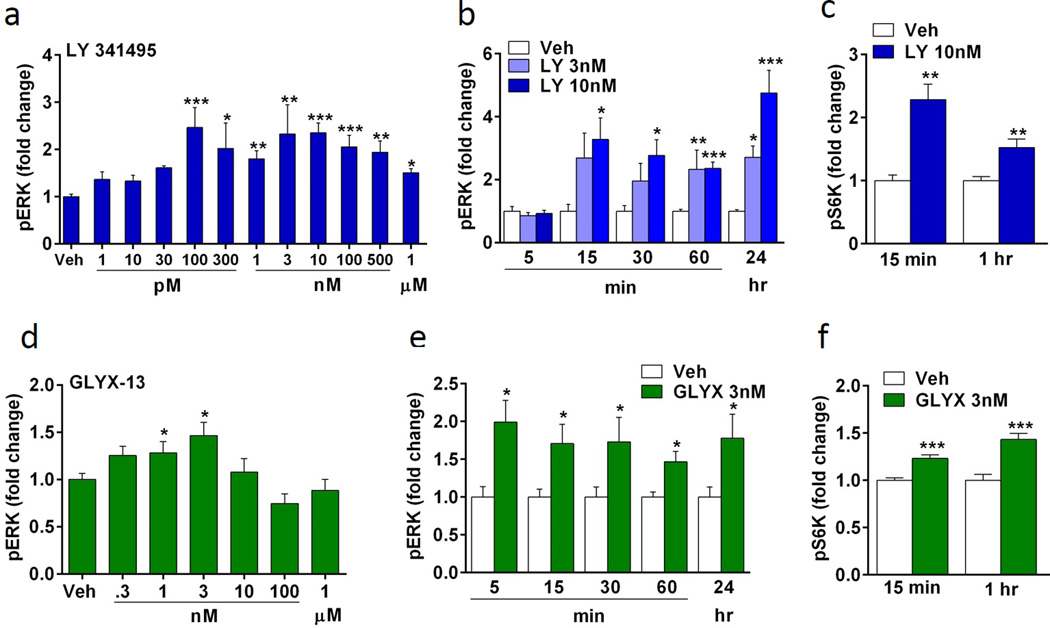
Figure 2. Incubations with LY 341495 or GLYX-13 increase phospho-ERK and phospho-S6K signaling in primary neuronal cultures.
(a) LY341495 increases phospho-ERK (pERK) in a concentration dependent manner. Following 1 hr incubation, 100 and 300 pM, 1 – 500 nM, and 1 uM increased pERK levels, determined by immunoblot analysis. (b) Concentrations of 3 and 10 nM LY341495 increased pERK activation in a time dependent manner. LY341495 10 nM rapidly increased pERK at 15 min with significant effects up to 24 hr. (c) LY341495 (10 nM) increased phospho-S6K (pS6K) following 15 and 60 min incubation, determined by immunoblot analysis. (d) GLYX-13 also produced a concentration dependent increase in pERK following 1 hr stimulation with 1 and 3 nM. (e) GLYX-13 (3nM) rapidly increased pERK at 5 min, and (f) increased pS6K following 15 and 60 min incubation. Levels of total ERK and S6K were determined to control for gel loading and membrane transfer. All results are presented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005, ***p < 0.0005 compared to vehicle (ANOVA and Fisher’s post-hoc least significant difference test for results in a–c and Students t test for D, F, E).