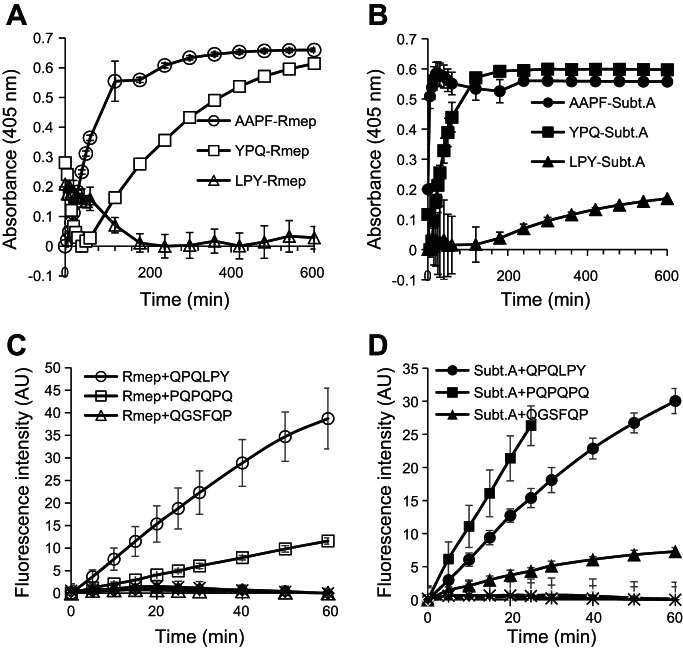
Fig. 4.
Cleavage specificities of Rmep and subtilisin A (subt A). A and B: hydrolysis of Suc-AAPF-pNA, Z-YPQ-pNA, and Z-LYP-pNA, each at 200 μM, by Rmep (A) and subtilisin A (B), each at 1 μg/ml. C and D: hydrolysis of gliadin-derived fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) substrates. FRET substrates containing QPQLPY, PQPQPQ, and QGSFQP, each at 100 μM, were incubated with Rmep (C) and subtilisin A (D), at 1 and 0.5 μg/ml, respectively. Controls were boiled Rmep and subtilisin A incubated with each of the three FRET substrates (no activity, baseline).