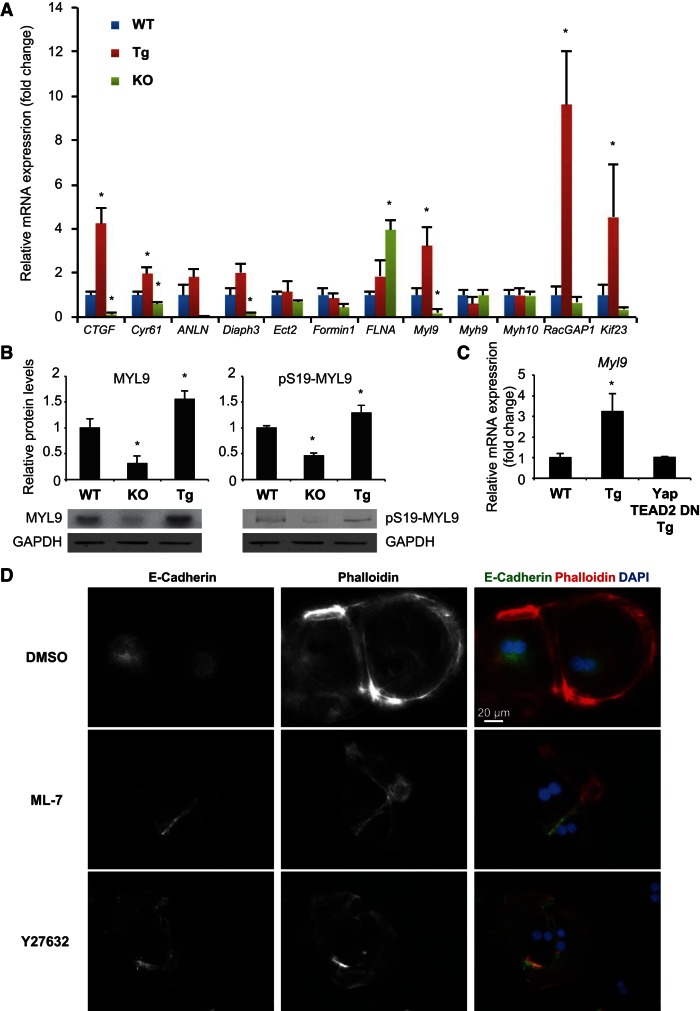
Fig. 7.
YAP promotes myosin light chain expression. A: graph shows the expression of genes of interest in day 1 hepatocytes from WT, Yap-KO, and Yap-Tg livers. Bars represent mean ± SE (n = 3 mice from each genotype). *P < 0.05, compared with WT by one-way ANOVA and unpaired t-test. B: Western analysis shows levels of MYL9 and pS19-MYL9 in day 1 hepatocytes from WT, Yap-KO, and Yap-Tg livers. Graphs show the quantification of MYL9, pS19-MYL9 protein levels. Bars represent mean ± SE (n = 3 mice from each genotype). *P < 0.05, compared with WT by one-way ANOVA and Fisher's least significant difference posttest. C: graph shows the expression levels of Myl9 in day 1 hepatocytes from WT, Yap-Tg, and Yap/TEAD2 DN-Tg mice. Note that YAP-induced Myl9 expression was inhibited by coexpressing a dominant negative form of TEAD2. Bars represent mean ± SE (n = 3 mice from each genotype). *P < 0.05, compared with WT using a one-way ANOVA and Fisher's least significant difference posttest. D: E-cadherin and phalloidin staining of day 1 Yap-Tg hepatocytes treated with DMSO (vehicle control), 5-μM myosin light-chain kinases inhibitor ML-7 and 25-μM Rho-associated protein kinase (ROCK) inhibitor Y27632 for 24 h. ML-7- and Y27632-treated Yap-Tg doublet hepatocytes show similar F-actin organization and E-cadherin junction formation as Yap-KO doublet hepatocytes.