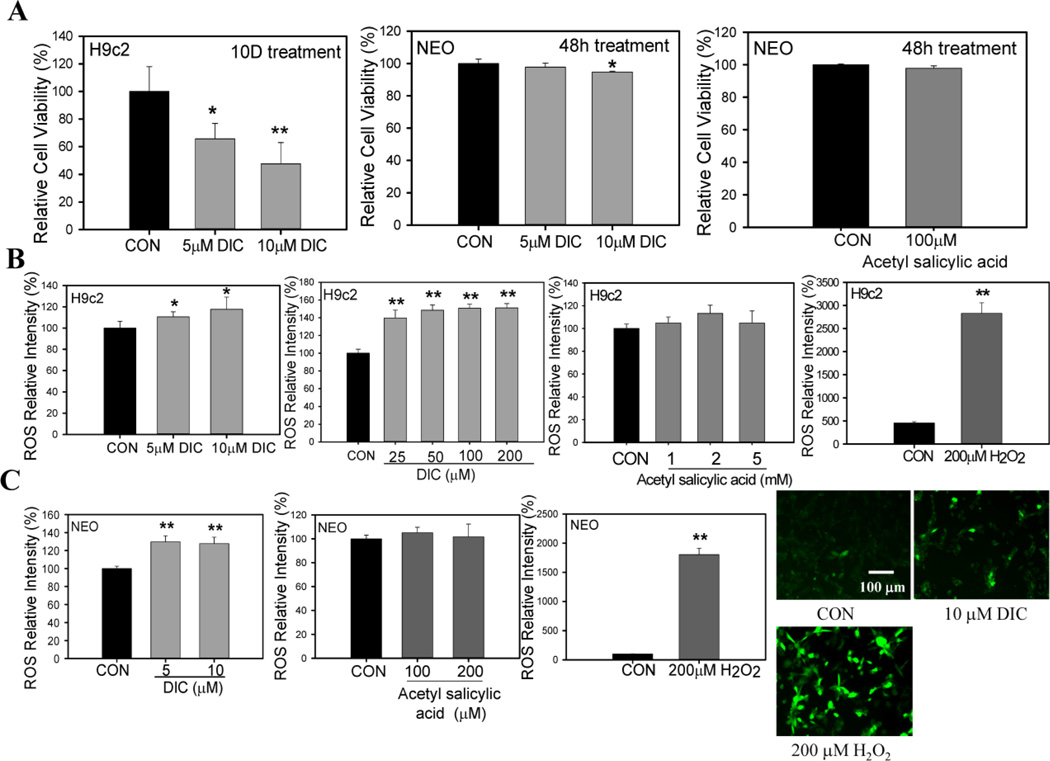
Figure 9. Diclofenac reduces cardiac cell viability and increases ROS production in H9c2 and neonatal cardiomyocytes.
A, H9c2 cardiac cells treated with vehicle or 5 and 10 µM diclofenac (DIC) for 10 days. Neonatal murine cardiomyocytes were treated with 10 µM DIC or vehicle for 2 days. Cell viability of H9c2 cells and neonatal cardiomyocytes were measured by Alamar Blue. Additionally acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin, 100 µM) was used to measure cell viability in neonatal murine cardiomyocytes. B, ROS levels in H9c2 cardiac cells treated with different concentrations of DIC (25 µM–200 µM) and acetyl salicylic acid (1mM–5mM). 200 µM Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) was used as a positive control for ROS production. C, Effect of 5 µM DIC, 10 µM DIC, 100 µM acetylsalicylic acid or 200 µM acetylsalicylic acid on ROS levels in neonatal cardiomyocytes. Fluorescent images represent ROS generation in the presence of DIC and H2O2. The images are a representative of 3 or more independent experiments. Results are expressed as mean ± SD (n=4–9), * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.001.