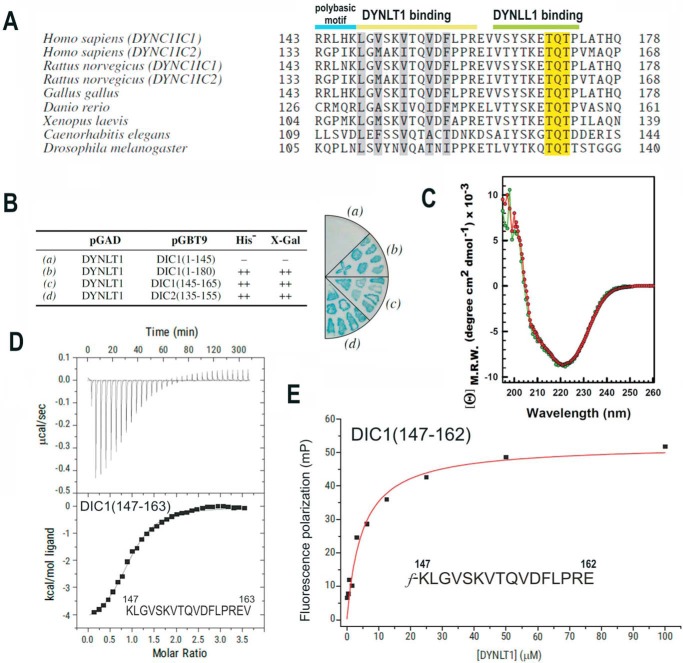
FIGURE 1.
Identification of the minimal DYNLT-binding region within dynein intermediate chain. A, sequence comparison between mammalian DIC isoforms and those of selected model organisms known to bind DYNLT1 and DYNLL1 consecutively. The polybasic motif and the DYNLT1 and DYNLL1 binding sites are shown at the top. The characteristic TQT motif present in many DYNLL1 binding partners is also shown. B, yeast two-hybrid assay using DYNLT1 in the bait plasmid and various dynein intermediate chain constructs. Growth in the absence of the amino acid His and presence of 3-aminotriazole and X-Gal activity are shown. The right panel shows a representative result of an X-Gal assay in a plate. C, circular dichroism spectra of purified recombinant DYNLT1 saturated with a DIC1 peptide (KLGVSKVTQVDFLPREV) (in red) and its self-saturated DYNLT1-DIC2 counterpart (shown in green) in the far-UV region. D, ITC analysis of the binding of a dynein intermediate chain peptide (KLGVSKVTQVDFLPREV) to purified DYNLT1. The thermogram is shown in the upper panel, and the binding isotherm is shown in the bottom panel. Curve fitting rendered a Kd value of 6.06 ± 1.3 μm. E, representative binding curve for a FITC-labeled dynein intermediate chain peptide (f-KLGVSKVTQVDFLPRE) to DYNLT1 measured by fluorescence polarization. A calculated Kd of 4.80 ± 0.5 μm could be obtained. Results are representative of three independent experiments. mP, millipolarization units; M.R.W., mean residue weight.