FIGURE 5.
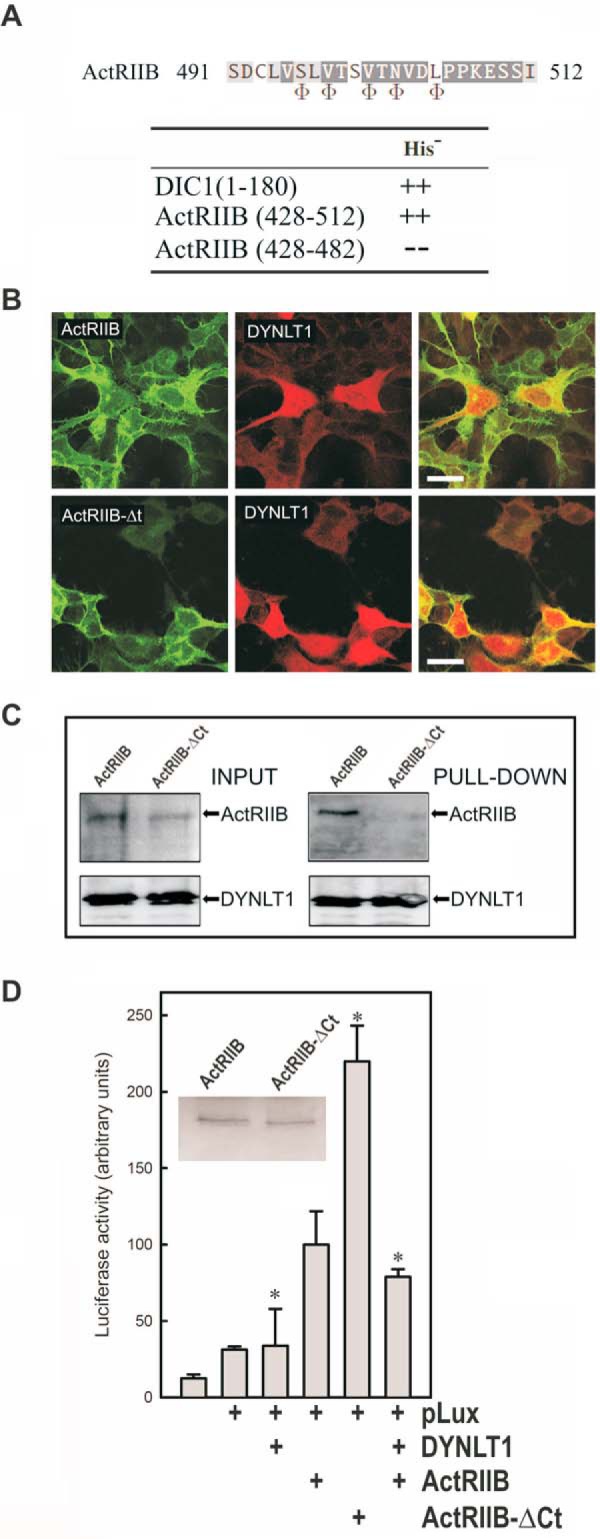
Binding of DYNLT1 to the intracellular C terminus of activin receptor IIB inhibits its signaling properties. A, sequence of ActRIIB at the binding site within the canonical groove of DYNLT1. The positions where hydrophobic amino acids are expected are shown at the bottom using the Φ symbol. Interaction between the C terminus of ActRIIB(428–512) and DYNLT1 in a yeast two-hybrid assay is shown. DIC1 was included as a positive control. B, confocal microscopy immunofluorescence of HEK293 cells transfected with mCherry-tagged DYNLT1 together with GFP-tagged ActRIIB constructs. The upper panels show full-length GFP-tagged ActRIIB, whereas the bottom panels show C-terminally deleted GFP-tagged ActRIIB. Merged panels are shown to the right in both cases. Scale bars, 25 μm. C, lectin-tagged DYNLT1 and full-length ActRIIB or its ActRIIB-ΔCt counterpart in transfected COS7 cells were allowed to associate, and the DYNLT1 moiety was sedimented with Sepharose beads. The appearance of each protein in the pellet fraction was determined with the appropriate antibodies. D, the effect of DYNLT1 on ActRIIB signaling was analyzed in transfected HEK293 cells using a luciferase reporter construct. The inset shows a Western blot of transfected ActRIIB and ActRIIB-ΔCt. All experiments were performed in duplicate wells and repeated three times. The results show average -fold changes and refer to transfected wild-type ActRIIB in the presence of p3TP-lux plasmid. S.D. values are indicated by error bars with * indicating p < 0.05.
