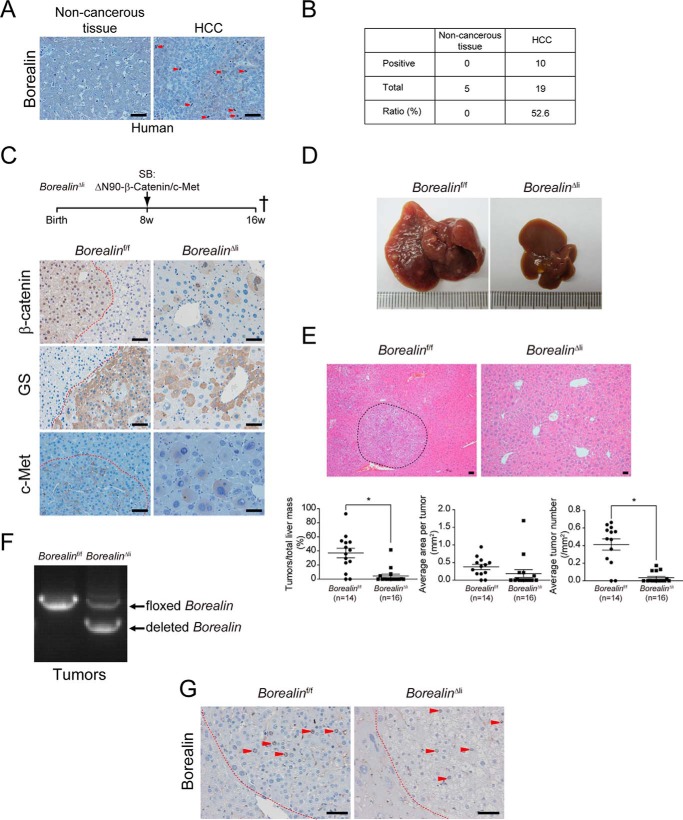
FIGURE 6.
Borealin deficiency inhibits ΔN90-β-Catenin/c-Met-induced HCC development. A, borealin protein levels were characterized by IHC staining in human HCC samples. Arrowheads indicate Borealin-positive cells. B, borealin positive ratio in human HCC samples was quantified. C, HCC was induced by the hydrodynamic transfection of plasmids encoding the Sleeping Beauty transposase and transposons with oncogenes of ΔN90-β-Catenin and c-Met in 8-week-old BorealinΔli and control Borealinf/f mice. These mice were sacrificed 8 weeks later to quantify the HCC mass. IHC staining showed that human β-Catenin protein and its downstream target glutamine synthetase (GS) were both highly expressed in the BorealinΔli and Borealinf/f livers 8 weeks after transfection. D, large amounts of HCCs developed in control Borealinf/f mice but not in BorealinΔli livers. E, H&E staining of liver sections from the BorealinΔli and control Borealinf/f mice. Liver cancers were encircled by dashed lines. Total tumor mass, tumor number, and tumor size were quantified. *, p < 0.05; t test. F, genotypes were determined by PCR using HCC genomic DNA. G, IHC staining showed that there were many Borealin-positive cells in HCCs of the BorealinΔli mice. Scale bars, 50 μm.