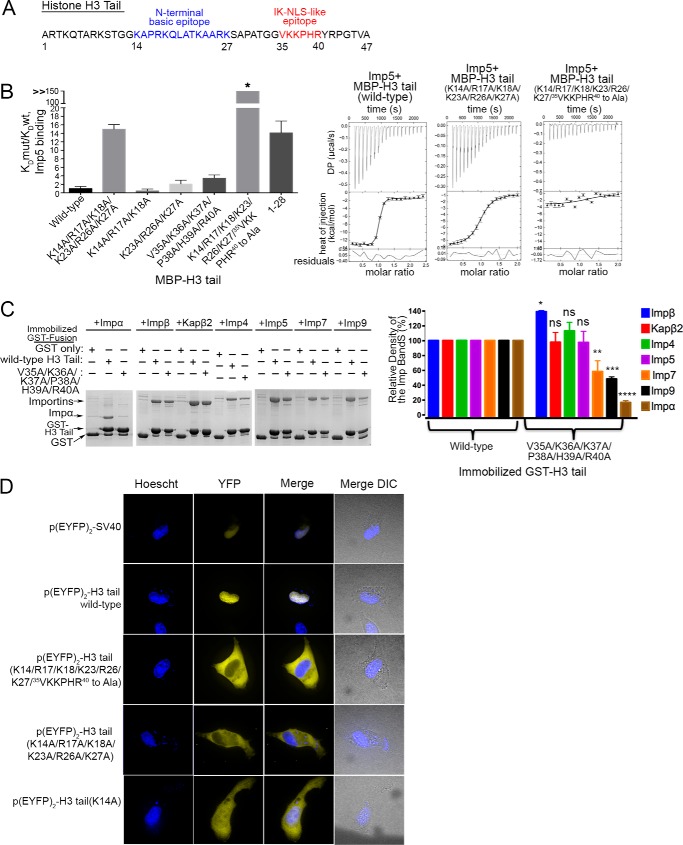
FIGURE 3.
35VKKPHR40 of the H3 tail contributes to binding Imp5, Imp7, Imp9, and Impα. A, a proposed Imp5-specific IK-NLS motif in H3 tail. B, ITC analysis of Imp5 and H3 tail showing that 35VKKPHR40 is also important for Imp5 binding. KD(mutant (mut))/KD(WT) for H3 tail mutants (KD values from triplicate ITC experiments) are shown in a histogram. C, pulldown binding assays of immobilized GST-H3 tail proteins (wild type and the H3 tail(V35A/K36A/K37A/P38A/H39A/R40A) mutant) with Impβ, Kapβ2, Imp4, Imp5, Imp7, Imp9, and Impα (SDS-PAGE/Coomassie). Relative densities of the gel bands from experiments performed in triplicate are plotted in histograms. t tests were performed to assess significance of changes in Importin binding for the 36VKKPHR40 to Ala mutation (ns, p > 0.05; *, p ≤ 0.05; **, p ≤ 0.01; ***, p ≤ 0.001; ****, p ≤ 0.0001). Error bars represent S.D. D, nuclear localization of EYFP2-H3 tail proteins in HT1080 cells. YFP (pseudocolored in yellow), Hoechst (pseudocolored in blue), and merged images were captured using spinning disk confocal microscopy of live HT1080 cells (100×). The image shown is a representative of four images.