FIGURE 6.
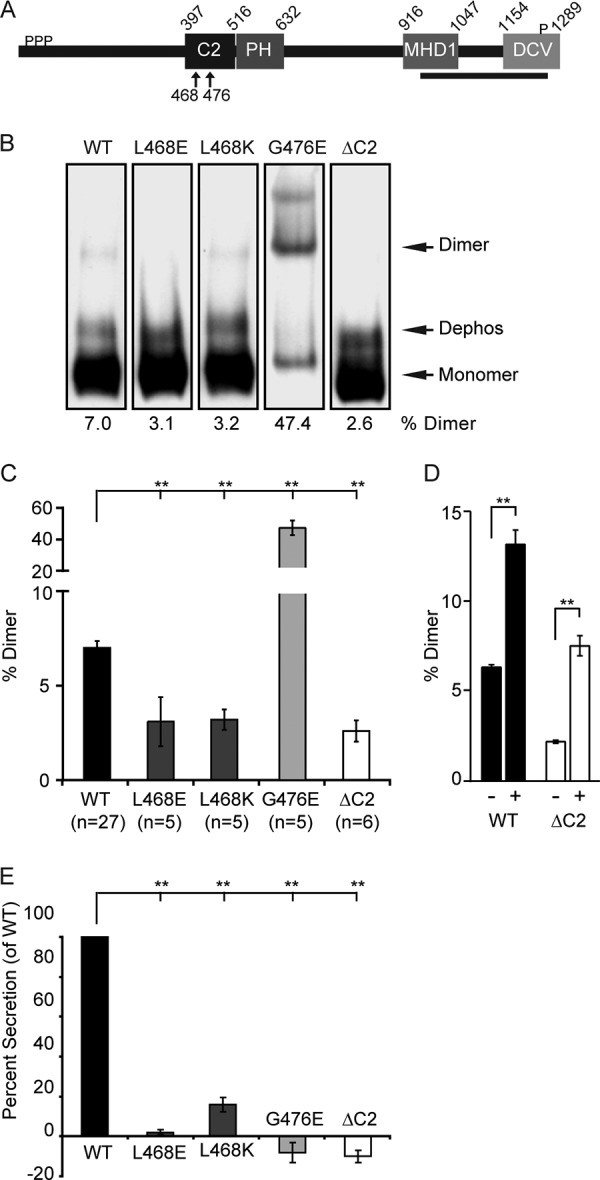
Loss of function CAPS mutants exhibit altered dimerization. A, domain architecture for R. norvegicus CAPS (NP_037351.1). C2 and PH domains were identified by multiple alignments in the SMART database. The MHD1 domain is from Ref. 25. The DCV binding domain is from Ref. 57. Ser phosphorylation (P) is from Ref. 31. CATCHR homology (boldface underline) is from Ref. 20. B, loss of function C2 domain mutants of CAPS exhibit abnormal dimerization. 100 ng of purified wild-type CAPS-Myc-His and mutants were analyzed by CN-PAGE and visualized by Western blot with Myc antibody. The CAPS-Myc-His band corresponding to dephosphorylated CAPS (Dephos) (31) was not routinely resolved from monomer in other CN-PAGE studies. C, the percentage of dimer for each protein indicated below each lane in B is plotted as histograms showing means ± S.E. (error bars) for the indicated n values. Comparisons with wild-type protein are indicated (**, p < 0.0001). D, wild-type CAPS-Myc-His and CAPS(ΔC2)-Myc-His were tested for dimerization in the absence (−) or presence (+) of PI(4,5)P2 as in Fig. 3C by BN-PAGE (**, p < 0.001; n = 3). E, activities of purified CAPS and mutants in a permeable cell secretion assay tested at 20 nm in triplicate (mean ± S.E.; **, p < 0.0001). Wild-type CAPS activity was set to 100%.
