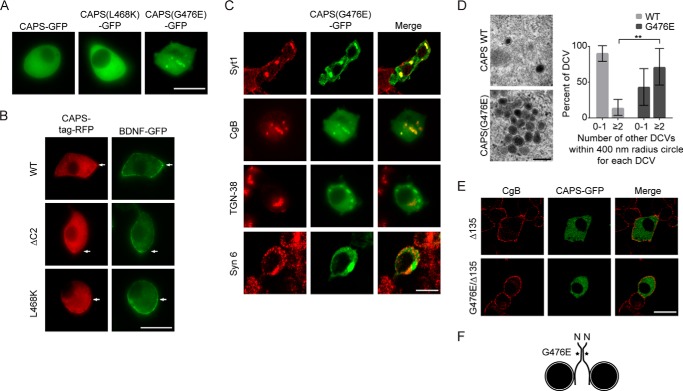
FIGURE 8.
Localization of CAPS C2 domain mutants in PC12 cells. A, representative confocal images of PC12 cells expressing wild-type or mutant CAPS-GFP fusion proteins. Wild-type CAPS and CAPS(L468K) are broadly distributed in the cytoplasm, whereas CAPS(G476E)-GFP localizes to large structures. Scale bar, 10 μm. B, confocal images of live PC12 cells expressing BDNF-GFP (vesicle cargo) and either wild-type CAPS, CAPS(ΔC2), or CAPS(L468K) as TagRFP fusions. Scale bar, 10 μm. C, confocal images of fixed PC12 cells expressing CAPS(G476E)-GFP and immunostained for dense core vesicle proteins synaptotagmin-1 (Syt1) or chromogranin B (CgB), for trans-Golgi protein TGN-38, or for Golgi and immature vesicle protein syntaxin-6 (Syn-6). Scale bar, 15 μm. D, electron micrograph of fixed PC12 cell expressing CAPS-GFP or CAPS(G476E)-GFP. An enlarged region containing clusters of dense core vesicles is shown. Scale bar, 200 nm. Clustering was determined by the number of additional vesicles in a 400-nm radius surrounding a vesicle; binning results for 0–1 or ≥2 vesicles/circle are shown. CAPS(G476E)-GFP (n = 7 sections) significantly increased the percentage of vesicles with ≥2 adjacent vesicles (**, p < 0.001) compared with CAPS-GFP (n = 8 sections). Error bars indicate S.D. E, CAPS(G476E) clustering of dense core vesicles is dependent on the vesicle binding domain of CAPS. C-terminal truncation of 135 residues from CAPS abolished vesicle clustering by CAPS(G476E). Scale bar, 15 μm. F, model of dense core vesicle clustering by CAPS(G476E) depicting C2 domain self-interactions and C-terminal vesicle-binding domain.