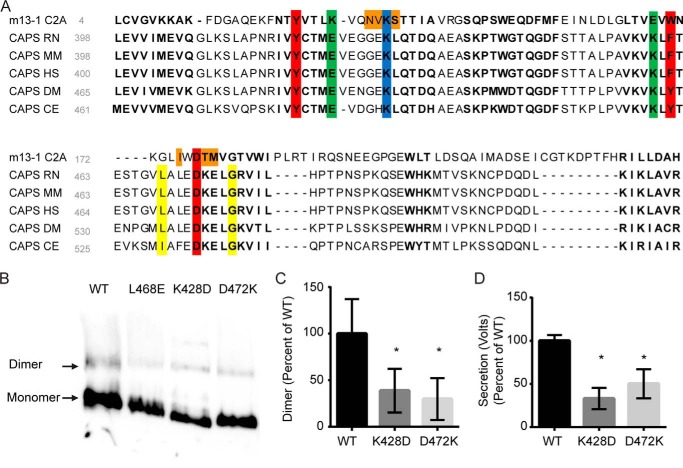
FIGURE 9.
Identifying conserved homodimerization motifs in Munc13-1 C2A and CAPS C2. A, sequence alignment of C2 domains generated by Cn3D. A spatially conserved residue alignment for C2 domains was created with 97 published C2 structures. This template was used to compare Munc13-1 C2A (Protein Data Bank code 2CJT), CAPS RN (R. norvegicus, NP_037351), CAPS MM (Mus musculus, NP_036191), CAPS HS (Homo sapiens, Q9ULU8), CAPS DM (Drosophila melanogaster, AAN06591), and CAPS CE (C. elegans, NP_001255666) sequences. Boldface type indicates residues that are spatially conserved across all 97 structures. Red and blue, partial chelation of a charged residue (lysine, blue) by 3 opposing residues (red) is conserved for Munc13-1 and CAPS. Green, electrostatic interaction between a lysine and glutamine is conserved spatially, although the residue positions are inverted between CAPS and Munc13-1. Orange, Munc13-1 homodimer interactions that involve residues with variable spatial positioning between C2 domains. Yellow, Leu-468 and Gly-476 residues identified in CAPS (22), where mutation causes loss of function. B, charge reversal mutations (K428D and D472K) in residues conserved in Munc13-1 C2A and CAPS C2 domains impair CAPS dimerization. Similar amounts of the indicated proteins were analyzed by CN-PAGE and Western blotting with CAPS antibody. C, data from B were quantitated, indicating decreased dimerization in K428D and D472K proteins compared with wild type (*, p < 0.05, mean ± S.D. (error bars), n = 3). D, CAPS(K428D) and CAPS(D472K) proteins were tested at 20 nm in the permeable cell secretion assay and found to be significantly impaired compared with wild-type CAPS (*, p < 0.05, mean ± S.D., n = 3).