Figure 3.
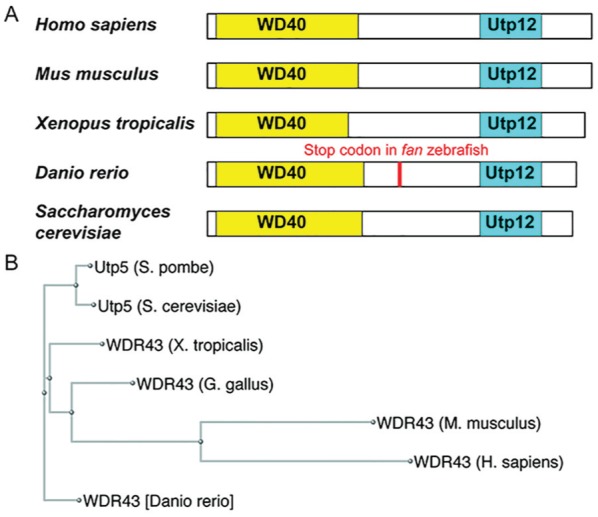
Evolutionary conservation of Utp5/WDR43. (A) Conserved WD40 and Utp12 domains predicted by the NCBI Conserved Domain database for Utp5/WDR43 in humans (Homo sapiens) and model organisms, including mice (Mus musculus), frogs (Xenopus tropicalis), zebrafish (Danio rerio), and yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae). White boxes indicate the relative lengths of the protein and are drawn to scale with the N-terminus to the left and C-terminus to the right. Yellow boxes indicate WD40 conserved domains (NCBI accession no. cd00200) and are drawn to scale. Cyan boxes indicate Utp12 conserved domains (NCBI accession no. pfam04003) and are drawn to scale. The location of the premature stop codon in fantome mutant zebrafish, which results in craniofacial developmental defects, is indicated in red. (B) Phylogeny tree for Utp5/WDR43 proteins. A ClustalW alignment of the indicated proteins was used to generate a phylogeny tree in the NCBI Genome Browser. This figure is available in color online at http://jdr.sagepub.com.
