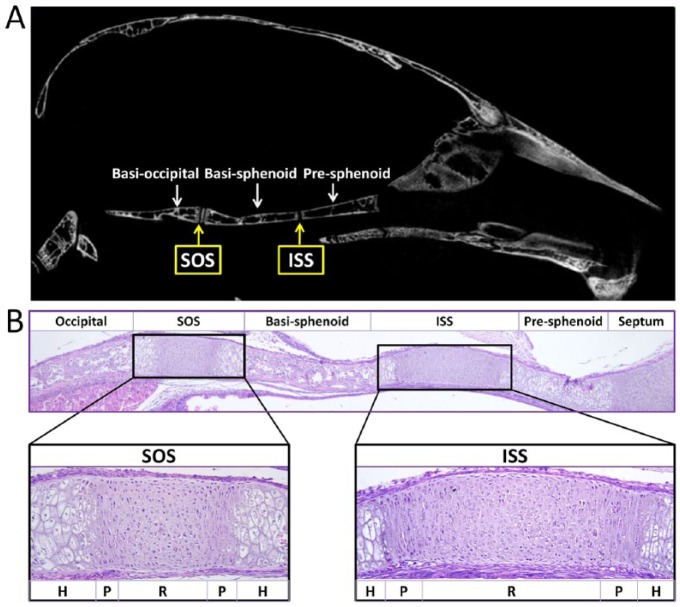
Figure 1.
The cranial base and synchondroses. (A) Micro–computed tomography image of the skeletal structures of the mouse cranial base at 2 mo of age. From the rostral side (right) to the caudal side (left), the cranial base of the mouse is composed of presphenoid, basisphenoid, and basioccipital bone. Between the adjacent bones are cartilaginous synchondroses, namely the intersphenoid synchondrosis (ISS) and the spheno-occipital synchondrosis (SOS). (B) Histological structures of the cranial base in a newborn mouse. Three ossification centers (occipital, basisphenoid, and presphenoid) are separated by 2 synchondroses: the ISS and the SOS. The synchondrosis is composed of mirror-image growth plates with a central resting zone (R), proliferative zones (P), and hypertrophic zones (H) on both sides.