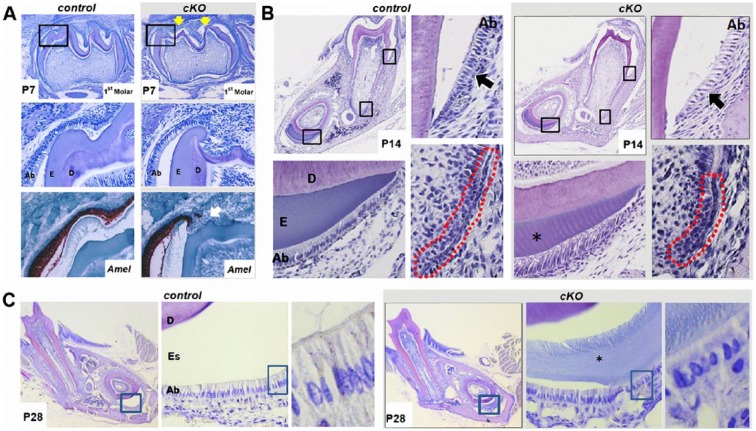
Figure 4.
Irf6-cKO (conditional knockout of Irf6) ameloblasts exhibit disturbances in adhesion, polarity, and enamel formation. (A) In postnatal day 7 (P7) samples, mandibular first molars are in the bell stage, and ameloblasts are actively secreting enamel matrix. In Irf6-cKO P7 mandibular first molars, irregular cusp morphology was observed (yellow arrows, first row). At higher magnification (middle row), the organization of the ameloblast layer appears disrupted near the cusps of Irf6-cKO mice, as observed by hematoxylin and eosin staining. In situ hybridization for amelogenin (Amel; red-brown color) further highlighted the disrupted ameloblast layer and mineralization. To account for variation caused by region and sectioning techniques, multiple samples and tooth regions were examined (n ≥ 4 for each group), and all Irf6-cKO sections exhibited similar ameloblast-layer alterations. (B) In P14 samples, enamel matrix deposition is normally complete in mandibular first molars, and in demineralized sections, the enamel is represented by an empty space. Ameloblasts are in the maturation stages. In the control sample, ameloblasts have shortened but remain polarized. Irf6-cKO ameloblasts appeared less organized, and increased spacing was observed between them (compare control and conditional knockout regions marked by black arrows). Hertwig’s epithelial root sheath (outlined in red) appears shorter in the Irf6-cKO samples versus controls. In incisor sections, the enamel layer was thinner (asterisk). Ameloblasts in control samples appear to have shortened and are approaching maturation stages, whereas in Irf6-cKO samples, the ameloblasts appear to exhibit the morphology of secretory-stage ameloblasts. (C) Enamel space is thinner in Irf6-cKO samples when compared with controls, and immature enamel matrix is present in Irf6-cKO incisors but absent in comparable control sections (asterisk). At high magnification, disturbances are readily apparent in ameloblast morphology and organization in P28 Irf6-cKO mice as compared with control animals. Ab, ameloblasts; D, dentin; E, enamel; Es, enamel space.