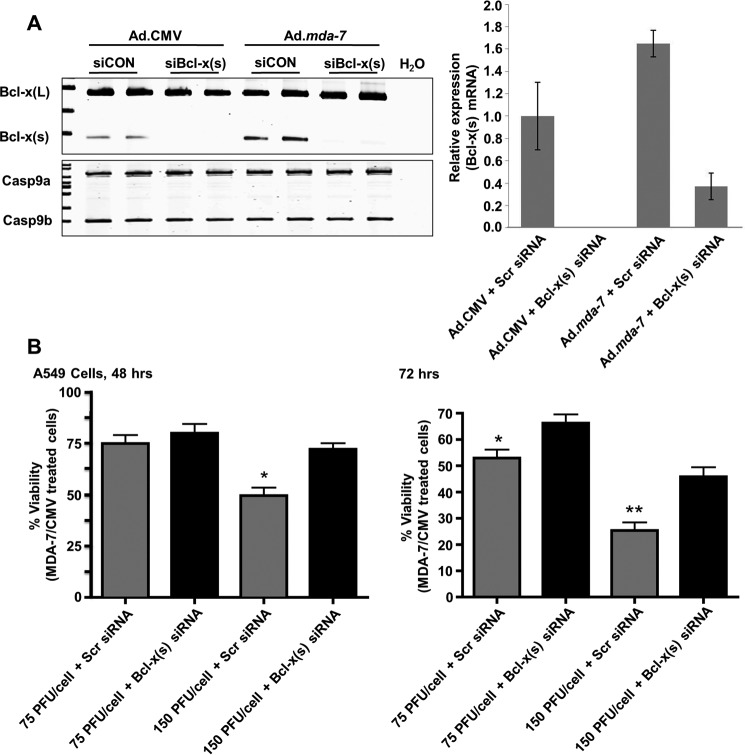
FIGURE 4.
Specific down-regulation of Bcl-x(s) mRNA significantly inhibits the loss of cell viability induced by Ad.mda-7. A, A549 cells (1.2 × 105) were transfected with Bcl-x(s) (siBcl-x(s), 100 nm) or control siRNA (siCON, 100 nm) and transduced with 150 MOI of either Ad.mda-7 or Ad.CMV control virus. After 48 h, total RNA was extracted and subjected to competitive (left panel) and quantitative (right panel) RT-PCR analysis of Bcl-x splice variants. The ratio of Bcl-x(L) to Bcl-x(s) mRNA was determined by densitometric analysis of RT-PCR fragments (p < 0.01, n = 6). The relative levels of Bcl-x(s) mRNA were determined as detailed under “Experimental Procedures” and normalized to 18s RNA. Data are expressed as mean ± S.D. and are representative of six separate determinations on two separate occasions. Scr siRNA, scrambled siRNA. B, A549 cells (1 × 104) were concomitantly treated as in panel A with the indicated MOI of either Ad.mda-7 or Ad.CMV control virus. After 48 or 72 h, the cells were assayed for cell viability using a WST-1 assay as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Data are expressed as mean of the percentage of viability of Ad.mda-7/Ad.CMV ± S.D. Data are representative of six separate determinations on two separate occasions. For the 48 h panel (left), * = p < 0.01 comparing lanes 3 and 4. For the 72 h panel (right), * = p < 0.01 comparing lanes 1 and 2 while ** = p < 0.01 comparing lanes 3 and 4.