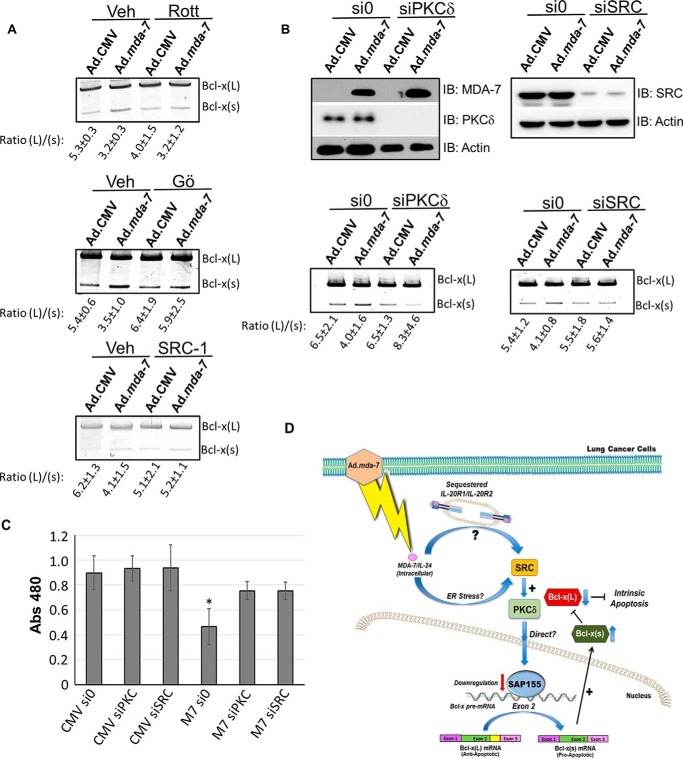
FIGURE 7.
Ad.mda-7 induces the activation of the Bcl-x(s)/proximal 5′ splice site of Bcl-x pre-mRNA via the SRC/PKCδ signaling axis. A, A549 cells were treated with Src inhibitor (SRC-1), pan-PKC-inhibitor (Gö 6983), or rottlerin (Rott) for the times indicated under “Experimental Procedures.” Cells were then exposed to Ad.mda-7 or Ad.CMV virus for 24 h. Cells were then harvested, and the ratio of Bcl-x(L)/(s) was determined. Veh, vehicle. B, A549 cells were transfected with either scrambled (si0), PKCδ (siPCKδ) or SRC siRNA (siSRC), and 48 h later, protein and RNA were harvested and the levels of SRC, PKC-δ, MDA-7, and actin, as well as the ratio of Bcl-x(L)/(s) mRNA, were determined. The ratio of Bcl-x(L) to Bcl-x(s) mRNA was determined by densitometric analysis of RT-PCR fragments. IB, immunoblot. Data are expressed as mean ± S.D. and are representative of three separate determinations on two separate occasions. C, A549 cells were exposed to either siRNA directed toward SRC or PKCδ for 48 h, and then exposed to MDA-7 for 24 h. Cells were then assayed using the WST-1 reagent as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Data are expressed as mean ± S.D. and are representative of six separate determinations on two separate occasions (* = p < 0.01, n = 6). D, schematic of how MDA7 suppresses cell survival by alteration of Bcl-x splicing via a SRC/PKCδ signaling pathway. Specifically, intracellular MDA7 expression promotes the activation of the Bcl-x(s) 5′ splice site via either an intracellular receptor event or ER stress to induce SRC and PKCδ activation, which may involve a direct or indirect effect of PKCδ on SAP155 (down-regulation) or other RNA trans-factors to up-regulate Bcl-x(s) level and down-regulate Bcl-x(L) level. As SAP155 is down-regulated by MDA-7 and cannot conclusively be determined as the regulatory RNA trans-factor, PKCδ is likely affecting Bcl-x 5′ splice site selection in an indirect fashion. The overall main theme of the study is that intracellular MDA-7 reduces cell viability through directly manipulating the level of anti-apoptotic Bcl-x(L) via affecting Bcl-x 5′ splice site selection, which requires the SRC/PKCδ signaling pathway.