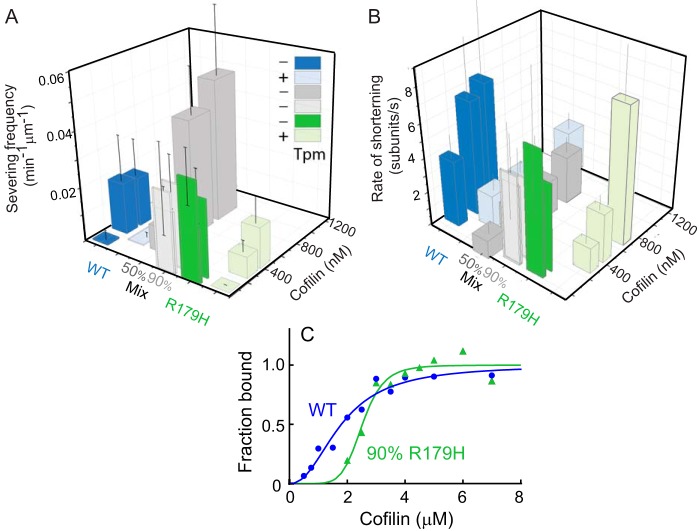
FIGURE 6.
R179H filaments are more susceptible to cofilin-induced shortening and severing than WT SM α-actin, even in the presence of tropomyosin. A, frequency of severing actin filaments by cofilin for WT SM α-actin (blue bar), R179H (green bar), and mixtures of WT and mutant actin (50% R179H, darker gray bars; 90% R179H, lighter gray bars). Lighter shaded blue and green bars are in the presence of smooth muscle tropomyosin. Frequency is reported as the number of events per 1 min per 1 μm of actin filament. Error bars are S.E. Equimolar copolymers of R179H and WT are more resistant to cofilin severing than R179H homopolymers. B, rate of actin filament shortening induced by cofilin. Same color scheme as A. Error bars are S.E. Equimolar copolymers of R179H and WT are more resistant to cofilin shortening than R179H homopolymers. C, affinity of WT (blue) and R179H (green, formed from 90% R179H actin and 10% WT) filaments for cofilin determined by an actin pelleting assay. Maximal binding was normalized to 1. Data were fit to the Hill equation. Kapp for WT filaments is 0.6 × 106 m−1 and 0.4 × 106 m−1 for R179H filaments. The Hill coefficient is 2.2 for WT and 6.9 for R179H.