FIGURE 1.
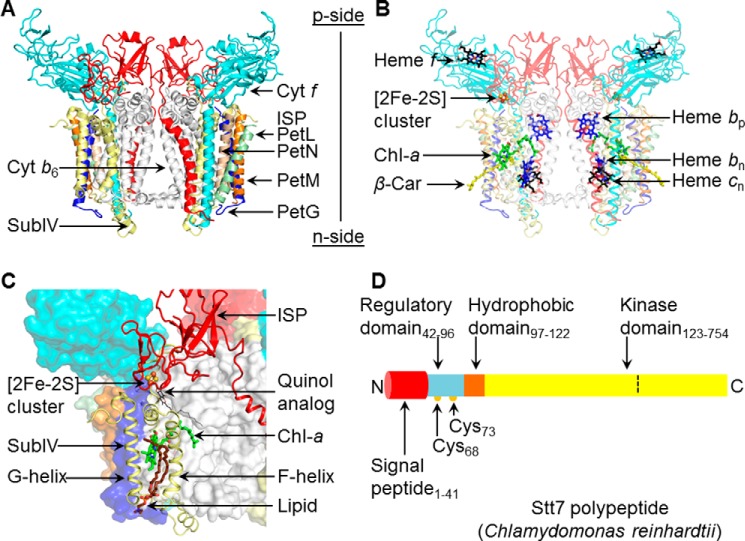
Summary: structure aspects of the cytochrome b6f complex and Stt7 kinase. A, the cytochrome b6f complex from the filamentous cyanobacterium Nostoc PCC 7120 (PDB code 4OGQ), consisting of eight distinct subunits (shown as ribbons). Cyt b6 (white) and subunit IV (yellow) are polytopic subunits containing four and three trans-membrane helices with seven prosthetic groups per monomer. Cyt f (cyan) and the Rieske ISP (red) contain a single trans-membrane helix and large p side extrinsic domains. Four single-helix trans-membrane subunits, PetG (blue), PetL (green), PetM (orange), and PetN (light brown), form the peripheral boundary of each monomer. B, electron transfer within the trans-membrane domain involves heme bp, bn (blue/red sticks) and heme cn (black/red sticks) and, on the p side, a [2Fe-2S] cluster (brown/yellow sticks, spheres) linked to the ISP subunit and covalently linked heme f (black/red sticks). Two pigments, Chl-a (green/red/blue sticks) and a β-carotene (β-Car, yellow sticks), are present in single copies in the trans-membrane domain. C, the p side Qp site is marked by a quinol analog (PDB code 2E76), shown as thin black/red sticks. On the p side, the Qp site is covered by the [2Fe-2S] cluster in the extrinsic domain of the ISP subunit (red). F and G helices of subunit IV (pale yellow) are located at the periphery. The phytyl tail of the Chl-a (green/blue/red sticks) wrapped around the F helix gates quinone residence at the Qp site (24). A lipid molecule (brown/blue sticks) is bound within the niche formed by F and G helices adjacent to the chlorin ring of Chl-a. Other protein subunits are represented in surface mode. D, schematic of the domain architecture of Stt7 kinase from the unicellular green alga C. reinhardtii, for which a crystal structure is not available. The Stt7 polypeptide consists of an N-terminal 41-residue signal peptide sequence (red) that targets the polypeptide to the chloroplast and is followed by a p side regulatory domain (blue, residues 42–96), containing two conserved Cys residues at positions 68 and 73 (yellow circles) implicated in the activation/deactivation of Stt7 (15, 18, 19). The single hydrophobic domain (brown, 97–122) is proposed (9) to span the membrane, connecting the regulatory and C-terminal kinase (yellow, residues 123–754) domains, the latter located on the n (stroma) side of the membrane. In this study, kinase activity was found to be restricted to residues 124–549 (defined by the dashed line), with residues numbered according to UNIPROT entry Q84V18.