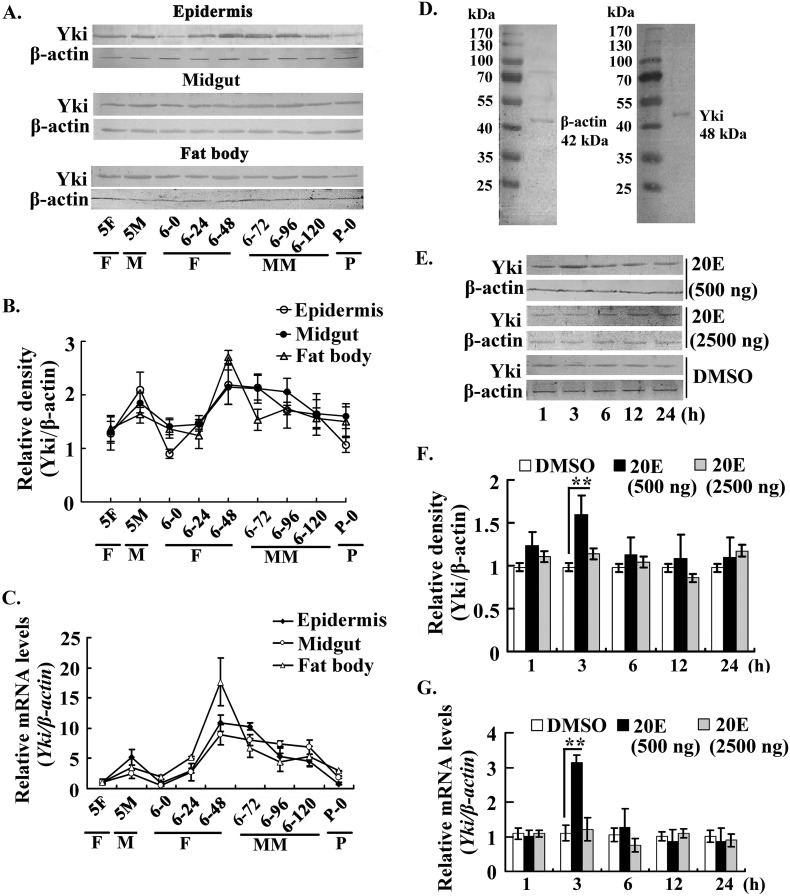
FIGURE 1.
Expression profile and hormonal regulation of Yki in tissues during larval development. A, Yki expression profiles in the epidermis, midgut, and fat body, as shown by Western blotting using a polyclonal antibody against H. armigera Yki. The gel concentration was 12.5%. 5F, fifth instar feeding; 5M, fifth instar molting; 6-0 to 6-120, sixth instar 0 h to sixth instar 120 h; P-0, pupal stage day 0; F, feeding; M, molting; MM, metamorphic molting; P, pupation. β-actin was used as a quantitative control using an antibody against H. armigera β-actin. B, quantitation of the images of Western blotting from three independent experiments using ImageJ software. C, qRT-PCR detected the mRNA levels of Yki in the epidermis, midgut, and fat body. D, protein ladder (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Lithuania) was used to identify the molecular weight of β-actin and Yki, respectively. The proteins in the midgut were used for Western blotting. The gel concentration was 12.5%. E, effect of 20E on Yki expression. Five μl of 20E (100 ng/μl or 500 ng/μl) was injected into the larval hemocoel of the sixth instar 6-h larvae for different times. An equal volume of diluted DMSO was injected as the control. The proteins in the midgut were detected by Western blotting. The gel concentration was 12.5%. F, the statistical analysis of the pictures in E from three independent experiments using ImageJ software. The values are expressed as the means ± S.D. (n = 3). **, p < 0.01 indicates a significant difference by Student's t test. G, qRT-PCR detected the mRNA levels of Yki after 20E induction. The experimental method was same as with E. β-actin was used as the control. Asterisks indicate significant differences (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01), assessed using Student's t test based on three replicates (n = 3).