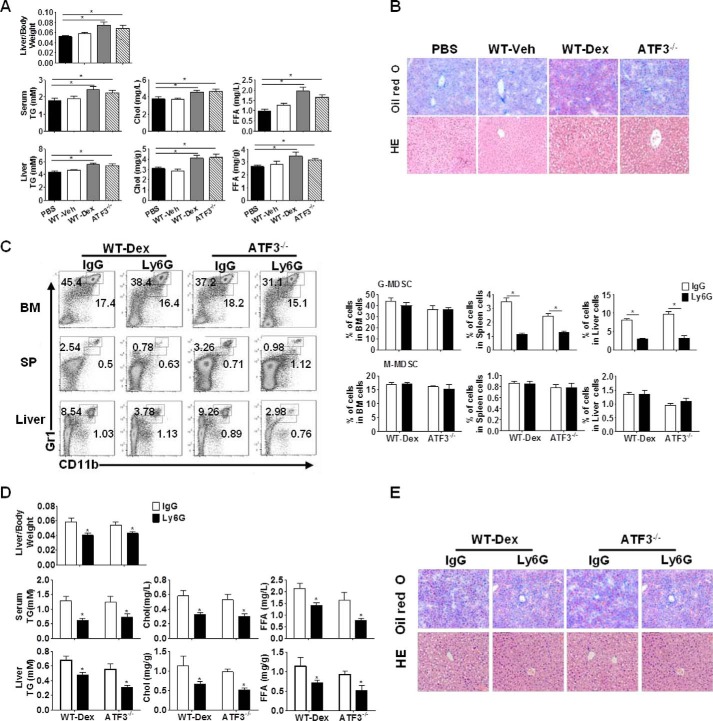
FIGURE 3.
ATF3 mediates the effect of G-MDSCs on GC-induced hepatic steatosis. A and B, G-MDSC adoptive transfer: G-MDSCs (3 × 106) from WT, Dex-treated WT (WT-Dex), or ATF3−/− mice were adoptively transferred into WT receipts (n = 6); mice were sacrificed at day 6. PBS was used as negative control. A, ratio of liver to body weight and the lipid contents. B, representative Oil-Red O and hematoxylin/eosin (HE) staining of liver sections were shown. C–E, G-MDSCs depletion assay: anti-Ly6G or anti-IgG antibodies were injected intravenously into Dex-treated WT or Veh-treated ATF3−/− mice, as described under “Experimental Procedures.” C, proportions of MDSCs were evaluated by flow cytometric analysis. SP, spleen. D, ratio of liver to the body weight, and lipid contents in the serum and liver tissue. E, representative Oil-Red O staining and hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining of liver tissue. B and E, original magnification, ×200. A, C, and D, data represent the mean ± S.E. of six mice per group of four independent experiments. *, p < 0.05, unpaired t tests.