FIGURE 2.
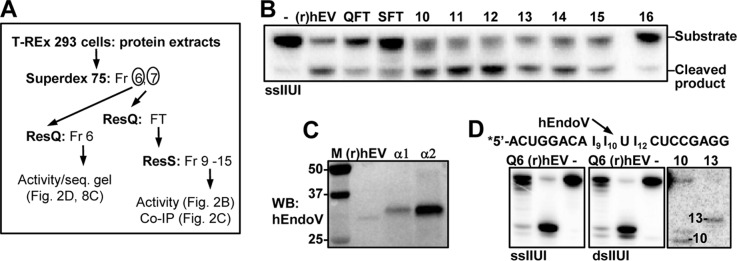
Activity of endogenously expressed hEndoV. A, purification scheme for endogenously expressed hEndoV using T-REx 293 cells as starting material. ResQ, Resource Q; ResS, Resource S chromatography; Fr, fraction; FT, flow-through. B, flow-through (QFT and SFT) and partly purified fractions (fraction 10–16) after ResS chromatography were probed for inosine-RNA (ssIIUI) cleavage activity. 1 μl from each fraction was used in the assays and recombinant (r)hEndoV (30 nm) as positive control. C, immunoprecipitation followed by Western blot analysis of endogenous hEndoV. Fractions 10 and 11 after ResS were diluted in IP buffer and supplemented with 2 μg of polyclonal (α1) or monoclonal (α2) hEndoV antibody. Precipitated material was run on SDS-PAGE, the gel was blotted onto a nylon membrane and proteins were detected with a third hEndoV antibody (polyclonal; α3). Recombinant hEndoV ((r)hEV, 20 ng) was included as a positive control in the Western blot (WB) analysis. Molecular mass marker (M) with sizes (in kDa) is shown to the left. D, cleavage products for endogenous hEndoV (Q6, ResQ Fr 6 T-REx) on single- and double-stranded IIUI substrates were run on 20% sequencing gels alongside with recombinant (r)hEV. Markers were RNA oligonucleotides of 10 and 13 residues. The sequence of the IIUI substrate and the preferred cleavage position for hEndoV is shown above the gel picture.