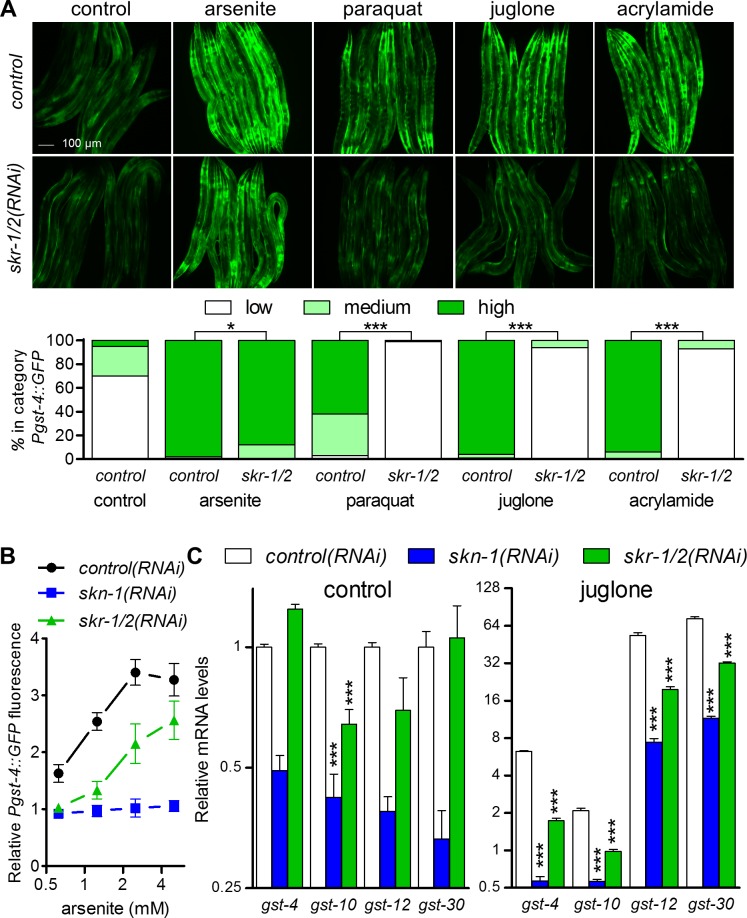
Fig 6. skr-1/2 is required for induction of SKN-1 dependent detoxification genes.
(A) Pgst-4::GFP fluorescence scoring and representative fluorescence micrographs of worms fed with control or skr-1/2 dsRNA after exposure to 5 mM sodium arsenite for 1 h (recovered for 3 h on NGM agar to induce GFP), 35 mM paraquat for 2 h (recovered for 2 h), 38 μM juglone for 3 h (recovered for 1 h), or 7 mM acrylamide for 4 h (no recovery). n = 70–89 worms from 3 independent trials, *P<0.05, ***P<0.001 as determined by Chi-Square test. (B) Relative Pgst-4::GFP fluorescence measured by a plate reader after a 6 h exposure to a range of arsenite concentrations; all values are normalized to control(RNAi) with no arsenite. n = 4–8 wells of worms in a 384 well plate; P<0.001 for skr-1/2(RNAi) and skn-1(RNAi) versus control(RNAi) at all concentrations except for the lowest. (C) Fold changes in mRNA of gst-4, gst-10, gst-12, and gst-30 relative to control (no stressors) in worms with control, skn-1, or skr-1/2(RNAi) after exposure to 38 μM juglone for 3 h. mRNA levels were normalized to rpl-2; values are means plus standard error of n = 4 replicates of 200–400 worms. All genes were induced significantly by juglone (P<0.001); ***P<0.001 compared to control (RNAi).