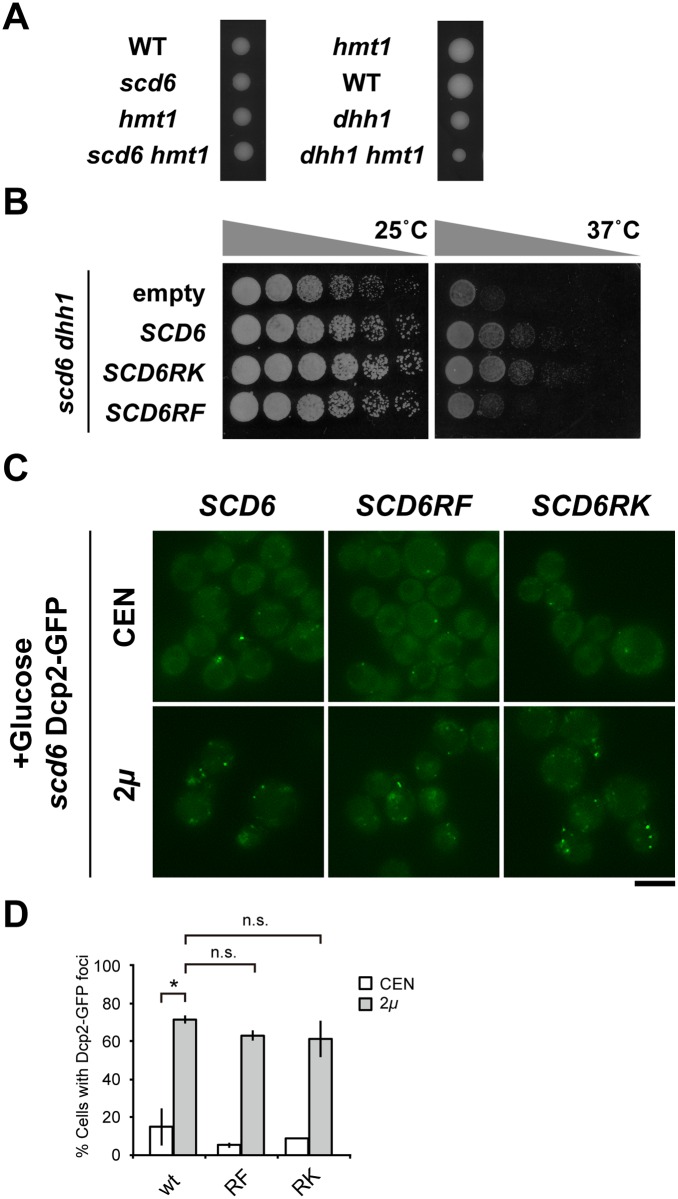
Fig 6. Hmt1 regulates Scd6 function.
(A) Growth of scd6 hmt1 and dhh1 hmt1 mutant strains. Strains that were heterozygous for scd6 hmt1 and dhh1 hmt1 were sporulated, and tetrads were dissected onto YPD medium. Growth was determined after 4 days at 25°C. (B) Growth assays; scd6 dhh1 mutant cells harboring empty vector (empty) or plasmids containing wild-type, methylation-deficient (SCD6RK), or methylation-mimic (SCD6RF) substitutions were spotted onto YPD medium and incubated at 25°C or 37°C. (C) scd6 Dcp2-GFP cells harboring YCplac33 (CEN) or YEplac195 (2μ) plasmids containing wild-type (SCD6), methylation-deficient (SCD6RK), or methylation-mimic (SCD6RF) substitutions were grown to mid-log phase in glucose-containing medium (+Glucose); Scale bar, 5 μm. (D) Percentages of Dcp2-GFP foci among more than 200 cells from three independent experiments are shown as means ± SD; *P < 0.05.