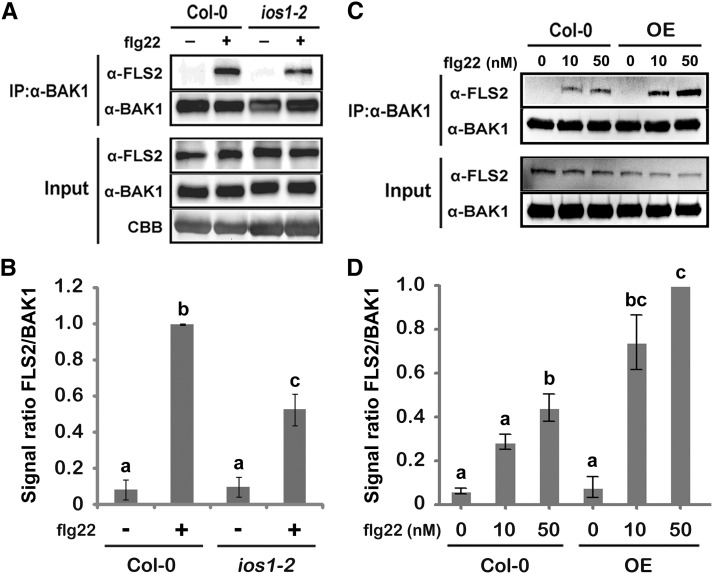
Figure 6.
IOS1 Regulates Ligand-Induced FLS2/BAK1 Association.
(A) and (B) Ligand-dependent association of FLS2 to BAK1 is reduced in the ios1-2 mutant. Col-0 or ios1-2 seedlings were treated (+) or not (−) with 100 nM flg22 for 10 min. Total proteins (input) were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-BAK1 antibodies and IgG beads followed by immunoblot analysis using anti-FLS2 and anti-BAK1 antibodies. For (A), Coomassie blue (CBB) is used to estimate equal loading (bottom panel). The experiment shown in (A) is one of three independent replicates pooled together in (B).
(C) and D) Ligand-dependent association of FLS2 to BAK1 is augmented in the IOS1-OE3 line. Col-0 or OE3 seedlings were treated with MgSO4 (0) or 10 or 50 nM flg22 for 10 min. Total proteins (input) were subjected to immunoprecipitation with anti-BAK1 antibodies and IgG beads followed by immunoblot analysis using anti-FLS2 and anti-BAK1 antibodies. The experiment shown in (C) is one of three independent replicates pooled together in (D). For both (B) and (D), signals were evaluated with the ImageJ software. Values are means ± sd of three independent biological replicates (n = 3). Different letters denote significant difference based on a one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Tukey HSD (P < 0.05).