FIGURE 1.
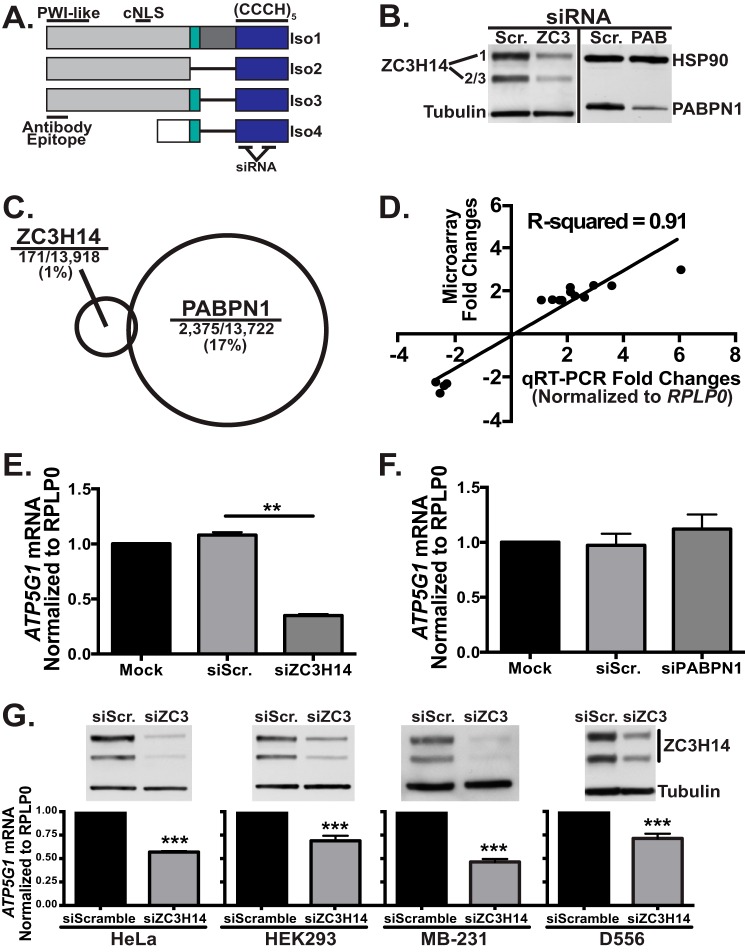
Knockdown of ZC3H14 decreases ATP5G1 mRNA levels in all cell types examined. A, ZC3H14 is alternatively spliced to form at least four distinct protein isoforms (Iso1–4), three longer isoforms (Iso1–3), and a shorter isoform (Iso4). All isoforms contain the C-terminal (CCCH)5 zinc finger domain (blue) that confers RNA binding. Isoforms 1–3 differ from one another only in selective inclusion of exons 10–12 (teal and dark gray). These isoforms all contain an N-terminal proline tryptophan isoleucine-like (PWI-like) fold as well as a predicted cNLS. Consistent with the presence of a cNLS, Iso1–3 are all localized to the nucleus at steady state. ZC3H14 isoform 4 contains a distinct N-terminal exon (white). As the cNLS is absent from this isoform, Iso4 localizes to the cytoplasm at steady state. The ZC3H14 antibody used in this study recognizes the N-terminal domain of isoforms 1–3 (Antibody Epitope). The siRNAs employed in this study target two independent sequences within the region that encodes for the CCCH zinc fingers. B, to assess knockdown, MCF-7 cells transfected with Scramble (Scr.), ZC3H14 (ZC3), or PABPN1 (PAB) siRNA were subjected to immunoblot analysis with ZC3H14 or PABPN1 antibody and control antibodies to detect tubulin and heat shock protein 90 (HSP90). Robust knockdown of ZC3H14 (∼75–80%) and PABPN1 (∼60–75%) was detected with no effect on tubulin or HSP90 (controls). C, total RNA isolated from MCF-7 cells transfected as in B was used for cDNA generation and hybridization to the Illumina BeadChip microarray platform. A schematic is shown indicating the relative number of transcripts that show a change (>1.5-fold) in steady-state level for each knockdown with size of circle representing fraction of transcripts impacted. Significance analysis of microarrays analysis revealed that 171 out of 13,918 (∼1%) of expressed transcripts in the transfected cells were affected (increased or decreased) by knockdown of ZC3H14 (101 increased and 70 decreased), whereas PABPN1 knockdown modulated 2,375 out of 13,722 (∼17%) expressed transcripts (1,285 increased and 1,090 decreased). D, fold-change values of select affected transcripts identified by the microarray analysis were plotted against fold-changes of the same select transcripts obtained by qRT-PCR analyses. Linear regression was used to determine the R2 value of 0.91, which represents a significant correlation between the results of both analyses and validates the effect on the transcripts analyzed. E and F, total RNA isolated from MCF-7 cells treated with mock transfection (Mock), Scramble siRNA (siScr.), ZC3H14 (siZC3H14, E) or PABPN1 (siPABPN1, F) siRNA was used for cDNA generation and qRT-PCR analysis with transcript-specific primers to detect ATP5G1 and the control RPLP0 mRNA. Knockdown of ZC3H14 (E), but not PABPN1 (F), results in a significant decrease in ATP5G1 steady-state mRNA levels. G, HeLa, HEK293, MB-231, and D556 cells (left to right) were transfected with Scramble or ZC3H14 siRNA. Transfected cells were subjected to immunoblot analysis to confirm knockdown (top) with ZC3H14 and tubulin (control) antibodies as well as qRT-PCR analysis (bottom) with ATP5G1 and RPLP0 (control) primers. Robust knockdown of ZC3H14 in each cell type resulted in a significant decrease in ATP5G1 steady-state mRNA levels. Values represent the mean ± S.E. for n = 3 independent experiments. ** and *** represent p ≤ 0.01 and p ≤ 0.001, respectively.